How does the Google Penguin Update Affects SEO and Negative SEO?
Over Optimization has been hitting websites like bowling pins – the score just keeps piling up. Google has now named this update the ‘Penguin’. I’m not entirely sure as to why. Sounds cute doesn’t it?
The Penguin update rolled out April 24, 2012 and started hitting some 3.1% of all English queries in Google Search. What is it really and what are the effects of the Penguin Update to SEO?
The Penguin Update increased the effectivity of Negative SEO
Negative SEO is what we can call ‘foul play’ among SEO specialists. This is a practice that some SEO specialists still implement in order to de-rank their competitors. With the Penguin update, Negative SEO’s effectivity was significantly increased. The Penguin Update takes three powerful factors into consideration for a penalty:
- Ratio of Exact Match Anchor Text in Poor Quality Articles
- Ratio of Bad Links coming from autoapprove, non-moderated blogs
- Ratio of No real On-site Activity by any visitors compared to inbound links
There were Negative SEO tests conducted after the Penguin Update. These tests proved that Negative SEO can still be done – and more so now that the Penguin update is in effect. Rand Fishkin even had an entire Whiteboard Friday dedicated to Negative SEO due to the aroused Negative SEO buzz from the Penguin Update.
In a nutshell, negative SEO was applied to seofaststart.com with the exact match anchor text ‘Dan Thies’. This was their rankings on March 22 before the negative SEO was applied:
seofaststart.com
- dan thies – number 1
- seo – number 11
- seo service – number 34
- seo book – number 3
This is was their method of applying Negative SEO:
- 18th March – seofaststart.com – blog posts started – anchor text “seo” “seo service” and “seo book”
- 22th March – seofaststart.com – 1 million scrapebox blast started – 100% anchor text “Dan Thies”
- 26th March – Dan Thies posts in Twitter that he has received an unnatural links message.
This was their rankings on April 18th after the Negative SEO was applied:
seofaststart.com
- dan thies – number 1 (still number 1)
- seo – not in top 1000 (down from number 11)
- seo service – not in top 1000 (down from number 34)
- seo book – number 34 (down from number 3)
Negative SEO can be a very powerful SERP rank killer if done correctly. Then again, it is foul play and is generally frowned upon in the SEO community. The sad fact of the matter is, Negative SEO practitioners are not doing the SEO industry a favor.
The Penguin Update raised the bar for Black hat SEO
I think that black hat SEO practices are unfair and should get penalized by the search engines because it does not bring in value to anyone. However, the Penguin update has taken getting penalized a bit further. In my experience with my clients, some of those sites bring in value to their visitors and yet they got hit.
Over optimization deals with more than just value. It deals with an intangible balance between the site’s brand authority and its SEO. As such, the standard to being ‘clean and neat’ in Google’s eyes have just been raised. People who are not doing anything fishy with their site need not worry in any way.
The way I see it, over optimization can be categorized as the most minute black hat practice – because optimizing your website beyond the value it brings in beats the idea of Google being a user-centric search engine.
The Penguin Update made way for the need to have strong branding and brand links
Need for strong brand signals has never been this important. Brand signal links have skyrocketed in value because of the Penguin update. If your links have zero brand links, there is a high chance that you are one of the sites that were affected by the Penguin update.
If you are one of the websites that got hit, try building brand links to your website to build trust and authority. These brand links will leverage your ‘allowability’ to have non-brand links (example: Exact match anchor text links). It will also ‘future-proof’ your site’s SEO.
The Penguin Update and Panda Update works together
I think there is a reason why the Panda update rolled out earlier than the Penguin update. It made way for the Penguin update to hit less sites. Panda hit more than 12% of all English queries while Penguin only hit around 3%. Don’t get me wrong, 3% is still big. But if Panda hadn’t rolled out earlier, this would have been much, much bigger.
Panda focuses on content. I think that content makes way for links to naturally come in. The way I see it, content creates linkable assets. Without real, solid, quality content, there should be little reason why you’re getting a lot of exact-match anchor text (high quality) links. Hence, in Google’s eyes, there should be little reason why you should rank.
So how do you get back from the Penguin Update?
For me, it just all goes back to basics. Create only what’s great. Great, unique, quality content. This can NEVER go wrong – especially by the way that Google is re-structuring the future of SEO. You have to think about future-proofing your SEO now. It’s not about how to rank high as fast as you can anymore. It’s about how to rank high and stay there.
Things are shifting in SEO. The focus has moved from competition and competitive linkbuilding into site’s development and user experience in a very short span of time. Google has been active now more than ever in their updates because SEO has been altering how websites rank in the Google SERPs in such a way that spam can take control if there is an extraordinary SEO specialist behind it.
Google will always be for the people because the money is where the people are. We should re-think our SEO strategies to go according to that simple fact.
Besides, more quality articles means more deep links – resulting to more social signals. I think this is the best way to go to recover your rankings if you got hit by the Penguin update.
I recently wrote an article about how you can recover from over optimization. You can check that out too.
Checking your Backlink Profile
I read a brilliant article from Cognitive SEO about how to identify low quality links – which I’m going to repost here for your reference. These tips are actionable and easy to understand. If you don’t have a cognitive SEO account, try it out now – it’s free!
Disclaimer: I am affiliated with Cognitive SEO as they are our backlink checking provider for SEO Hacker School
1. Link Networks
Over 90% of the Link Networks are easy to spot, both by the human eye and by the Google algorithm.
Most Link Networks have the following common patterns:
- Architected from Blogs and Forums, because they are easy to automate and replicate.
- Links try to look as natural as possible by being put inside the content of a blog post or forum thread.
- The owner of a link network rarely puts the effort to generate links back to each of the generated blog posts. This means that each and every post has a probability of having 0 or a small number of backlinks pointing to them.
- Each site from the link network, links out to at least 2 common money sites.
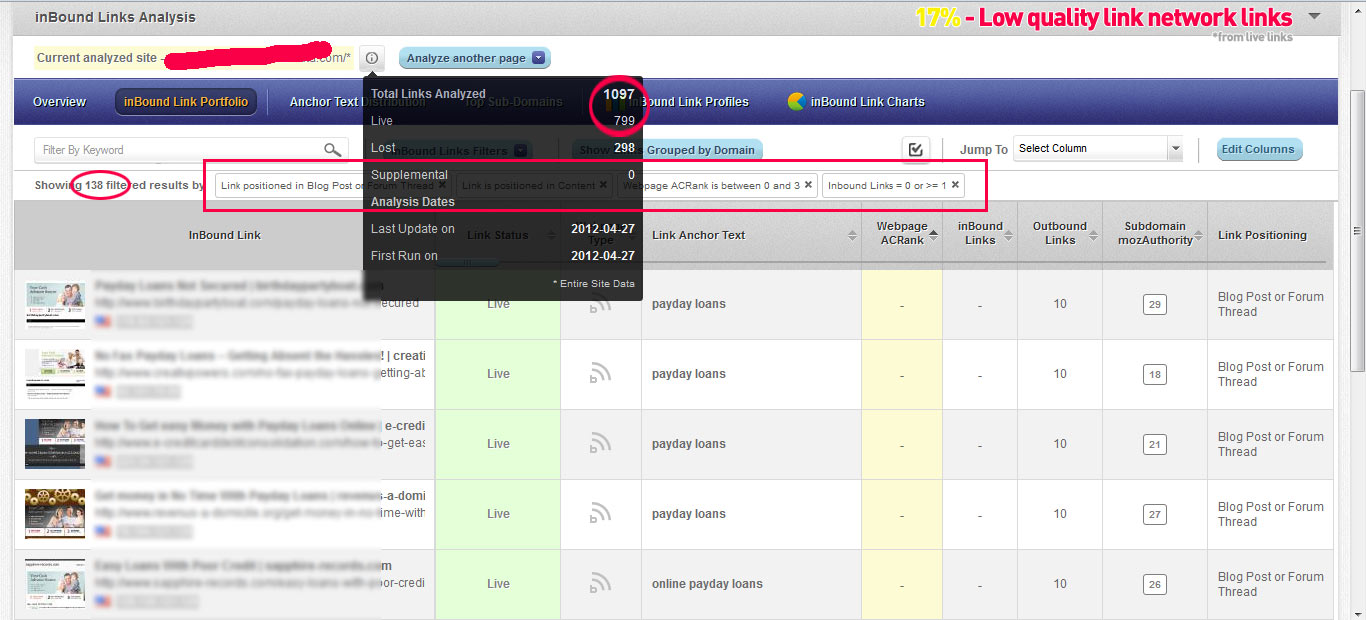
To find the links coming from link networks to your site you need to filter down the backlinks by blog posts and forum thread links, that are positioned in content, and have a low metric (Pagerank, Mozrank, ACrank etc) and a low number of incoming links to the actual backlink. The hardest part is to filter large lists of links by in Content and type of link (blog post, forum page etc). You can either do it by hand or use a tool that has the ability to make these classifications.
Quickly identify backlinks coming from Link Networks
Using cognitiveSEO go to the inBound Link Portfolio area, inside the inBound Link Analysis module, to view all the analyzed links. Apply the following filters:
- Link Position = Blog Post or Forum Thread
- Link Context = Content
- Majestic AC Rank = none or very low
- inBound Links = none or very few
Order ascending by Majestic AC Rank, so that you see the lowest quality pages first. Browse a bit through the links and use the link preview feature to quickly preview those pages. In our case we found 138 low quality links coming from different pages on various link networks.(17% of their entire backlink profile)
Any of the following types of links can be both natural or artificial. The difference is how they were acquired in terms of link velocity and link distribution over the entire backlink profile of a site.
To identify if your backlink profile is unnatural you should always compare your site to your competitors and check for major discrepancies between the backlink profiles of those sites. How I usually do it, is compare my site with the top 5 leaders in the industry and then compare my site with 5 other sites that are trying to break into the niche. There are always things that come up when doing such in-depth analysis. You should always compare metric distributions such Pagerank, mozRank or Majestic AC Rank. These are only the basic comparisons that you can make. The more advanced ones are when you start to compare links classified by webpage type, link type, in content versus not in content links, link position …
This was a short intro to the following type of links that we will analyze below.
Footer links are totally legit, when they appear in a natural number, correlated to the distribution of the visual positions on a page, of all your backlinks.
When these numbers tend to go up, and there is no other competing site in your niche that has stood the test of time in the same SERP positions, than this will raise a red flag to Google.
Usually footer links are aquired from sites that:
- sell links
- are involved in link exchange schemes
- have widgets or plugins installed (usually for SERP manipulation)
- “powered by” links ( ex : WordPress)
- partners of your business
- clients that link back to you
If you only find a few links compared to your entire backlink profile than there is no real problem here. If instead you get a long list of links, you might have a problem. There are situations when Google does not flag footer links … BUT … no one says that they are not discarded from Google’s ranking algorithm. One situation is for Godaddy, where they have almost 90% of their links coming from footer links. We checked their site with our tool after we saw the post by Yoast where he explained “GoDaddy’s spammy link building techniques”.
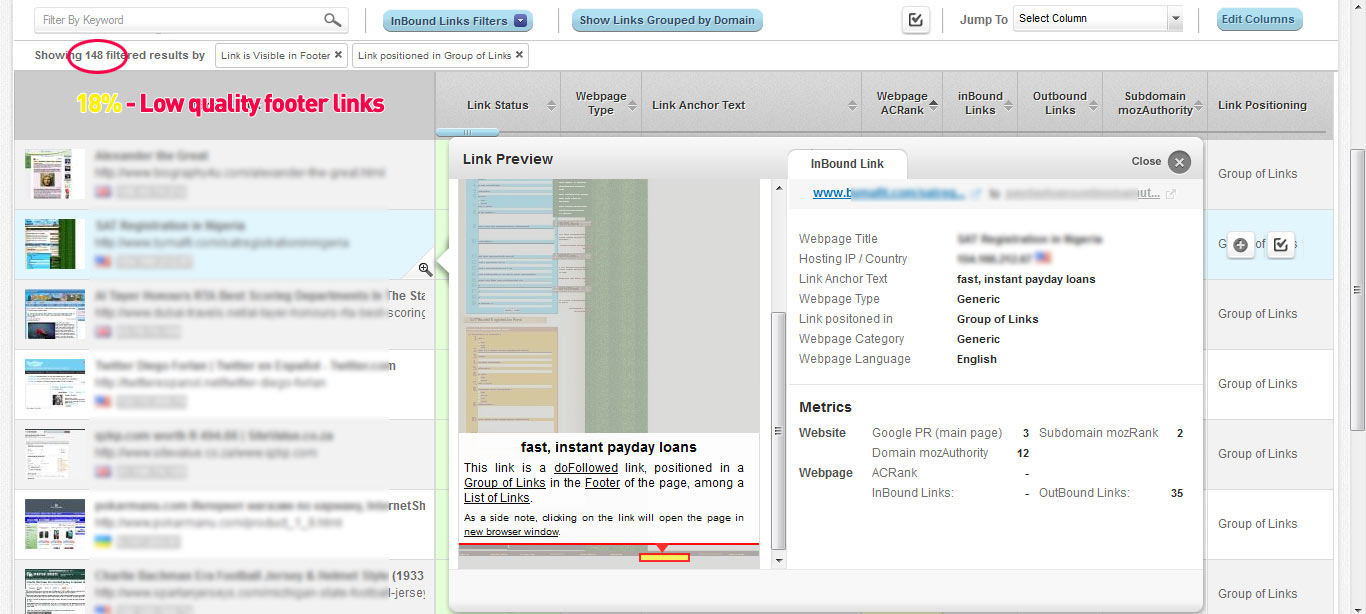
Quickly identify Footer Links
In the inBound Link Portfolio area apply the following filters:
- Link Visibility = Footer
- Link Context = Group of Links
This will select all the links that appear in blocks of links in the footer of the linking pages. We need to apply the “Group of Links” filter so that we do not have invalid results (links that appear in blog posts that are in the footer area of the page … ). For the site we analyzed we extracted 148 low quality footer links. (18% of their entire backlink profile)
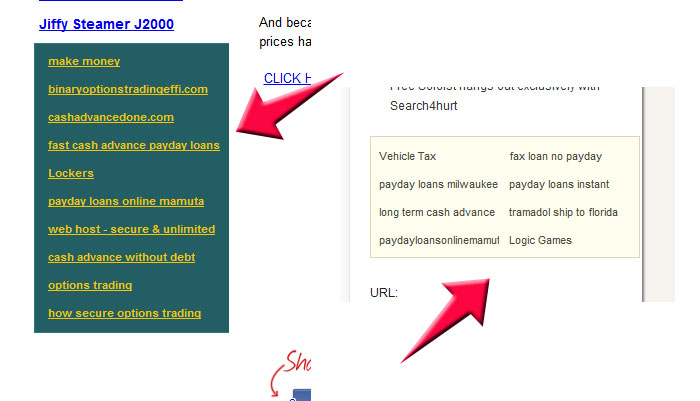
3. Blogrolls & other Blocks of Links
Blogrolls were abused so much, that they tend to be very carefully analyzed by the Google algorithm nowadays…
This category includes both blogroll links and groups of links that do not fit into the blogroll pattern. Here is such an example that is used to abuse the search engines and is not a blogroll. These examples are widgets that are installed on various website and where webmasters get place their link. They might also be considered a “link network” but a public one with no exact control of who includes the widget on the site. Too many links that fit these patterns, might be viewed as unnatural by the Google algorithm and you might get penalized for them. Some of those links can be sitewide links or not.
Advanced link widget networks will be carefull to not have those links listed as site-wides, as they might get flaged faster. Like with all of the other types of links presented in this guide, it all comes down to how they integrate in your link profile.
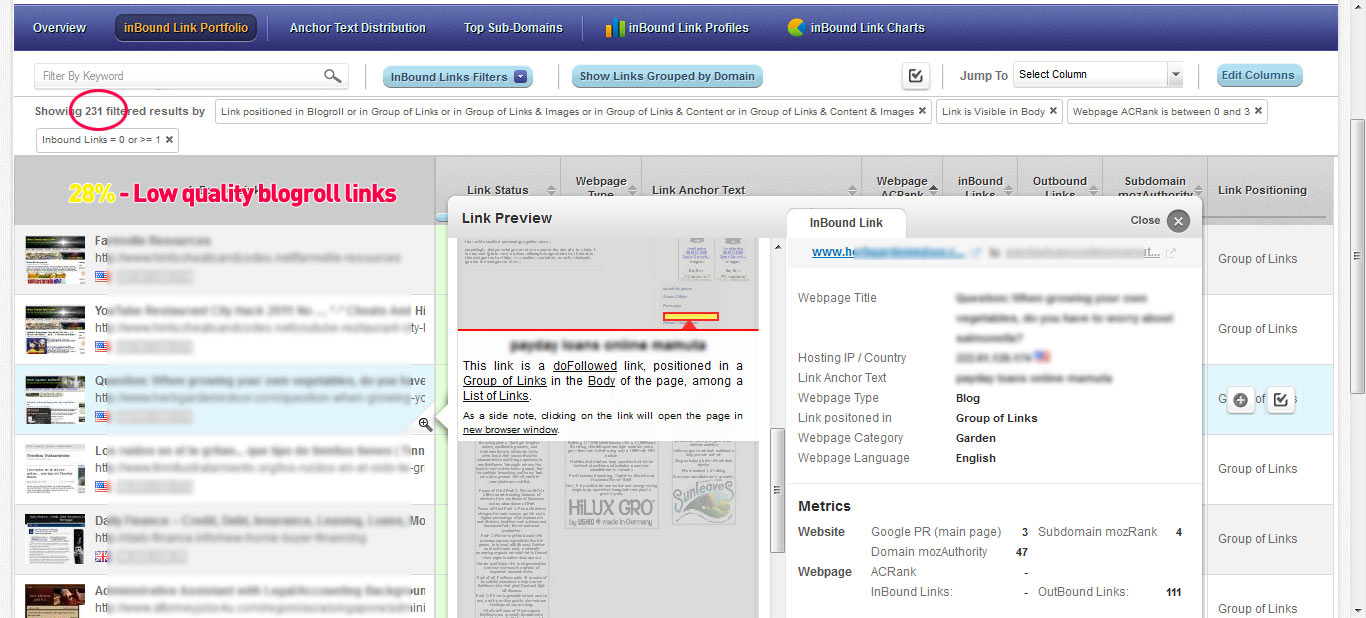
Quickly identify Blogroll & Groups of Links
Apply the following filters:
- Link Position = Blogroll, Group of Links, Group of Links and Images …
- Link Visibility = Body
- Majestic AC Rank = 0 to 3
- inBound Links = 0 to 100
You will get another list of low quality links that might hurt your rankings. In our case we got another 231 low quality links. (28% of their entire backlink profile)
4. Site-wide Links
Site-wide links can hurt your rankings
Site-wide links are old news on the Google landscape. Site-wides are devalued and can hurt your rankings for quite some time now. If your domain does not have the necessary authority and receives a couple of site-wides from some low quality sites, your site will be likely to be penalized by Google.
The idea behind the site-wide links is quite simple. It is more important to have more root domains talk (link) about (to) your domain, than to have many links coming from fewer root domains that talk (link) about (to) your domain.
The exception that confirms the rule. Of course there are site-wide links that will not hurt your rankings, and it all depends on the site the site-wide is put on. If that site is considered an authority and that site-wide link is not correlated to other factors such as high link velocity, than that site-wide could help you.
Quickly identify Site-Wide links
Go to inBound Link Charts / Sitewide Chart.
You will get a chart with the distribution of sitewide links. If it is a rather high number, click the pie and check those links individually. In our case we got 21% sitewide links.
Note: A site-wide link is considered to be a link that is automatically replicated across a large number of pages from the same site. Do not miss classify a site-wide as 10 different link coming from 10 different articles on Techcrunch for example. Those are not considered site-wides. Our software has a built in algorithm that matches different patterns and concludes is a link is a TRUE SITE-WIDE or not.
5. Blog Comments
Blog comment spam evolved on the back of the search engines.
Comment spam is a form of spamdexing and it exists since the beginning of the internet. There are several tools that help the spammers post comments automatically with the final aim to reach higher rankings in the search engines. That is why most of the comments are marked as No-Follow by the blogging platforms, so that Google will not index them. Still spam commenting is a huge phenomenon and everyone that owns a blog knows the amount of comment spam they receive.
Quickly identify Blog comment links
Apply the following filter:
- Link Position = Author name of a Blog comment, Content of a Blog comment
If you got mixed results you should also apply a metric filter, such as AC Rank between 0 and 3, to exclude higher quality pages. You could go even further and apply the Dofollow/Nofollow filter to see which blog comment links are followed. You can easily find both nofollow and dofollow links that are coming from blog comments.
6. Forum profile links & signatures
Forums are abused the same way blogs are.
 Having people discuss around your site in forums is the most natural thing that can happen to a site. It means your site generated some buzz in its niche. If you are doing link building using fake forum profiles, signatures and posting content and links automatically on forums this will appear in your backlink profile and could hurt your ranking when Google will flag it. These kind of patterns can be easily identified by Google.
Having people discuss around your site in forums is the most natural thing that can happen to a site. It means your site generated some buzz in its niche. If you are doing link building using fake forum profiles, signatures and posting content and links automatically on forums this will appear in your backlink profile and could hurt your ranking when Google will flag it. These kind of patterns can be easily identified by Google.
Quickly identify Forum links
Apply the following filters:
- Webpage type = Forum
- Link Position = Blog post or Forum thread.
This will identify links coming from forum threads. If you want to check signatures and profiles you should search for Link Position = Short Paragraph of Text, Group of Links.
7. Web Directory links
Forget Web Directory submission services that promise hundreds of directory registrations.
Having too many links coming from web directories is not always a good sign. This might raise a flag to the Google algorithm. You do not need hundreds of directories to be listed on, only a few quality ones that are well known in your niche. Doing hundreds of directory submissions, either manually or automatically, even if you do it on a longer period of time, so that it will not raise the link velocity flag, it will still ban you if those links are a big percentage of your backlink profile.
Quickly identify Webdirectory links
Apply the following filters:
- Webpage Type = Webdirectory
If you get a long enough list and that represents a big percentage of your inbound link profile than this might signal a problem that you need to investigate even further. Demo filtering here.
8. Article Directory links
Avoid cheap content!
This is the best advice you could get. Having too many links from article directories is again a sign that something unnatural is going on. Article directories and the sites they linked to mostly, were already hit by Panda last year. Below is one way to find your article directory links so that you can further investigate them.
Quickly identify Article Directory links
Apply the following filters:
- Webpage Type = Article Directory
- Majestic AC Rank = none or very low
- inBound Links = none or very few
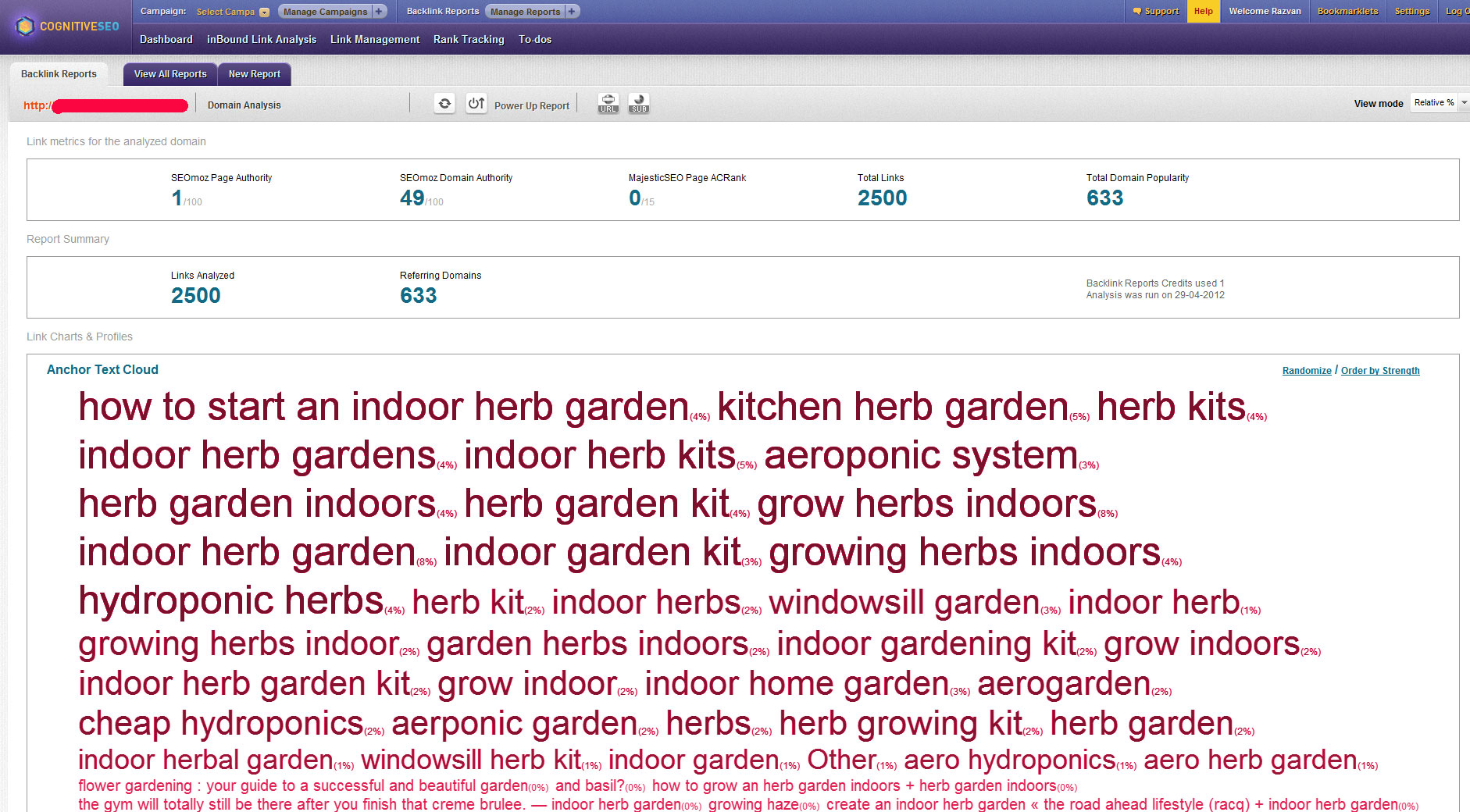
9. Anchor Text Distribution
Over optimized anchor text does not look natural at all!
Anchor text is either:
- brand keywords (domain name keywords or the actual brand name)
- money keywords
- navigational keywords (click here etc)
A natural distribution of anchor text would look like this.
An artificial anchor text distribution looks like this.
If your anchor text is over optimized, you are likely to be hit by Google.
I hope the tips above will help you identify the links that generated your problems with the Google Penguin update, but most importantly use these tactics to find those links and remove them before Google takes action and penalizes your site.
Tips for Keeps: If you got it, chances are you are doing something wrong. Check out your link profile using cognitive SEO or any other backlink checking tool, take away low quality links and build new, high quality ones. Support this strategy by creating great content and you’ll be fine.