Google: Robots.txt to Become an Official Standard After 25 Years
In a series of tweets by Google Webmasters, they have announced their proposal of a draft stating that Robots.txt is well on its way from becoming a de facto standard to an official one.
To quote Martijn, “This is especially handy if you have large archives, CGI scripts with massive URL subtrees, temporary information, or you simply don’t want to serve robots.” The mastermind of the initial standard saw fit that Robots.txt should come to light when he noticed that crawlers started going into his site in an overwhelming manner.
25 years later, this is still true today. Who knew that injecting a simple text file into your server can make bots easily see the content that you would want to serve to users? Precisely what SEO is all about.
Telling the bots what pages to access and index on your website makes it simpler for you to become visible in the SERPs. I should know since I make sure to properly implement the Robots Exclusion Protocol (REP) for sites. As one of the general and vital components of the web, it should be a cause of alarm if you are not familiar with REP and Robots.txt today.
At this point, we all learned all there is to know about Robots.txt but what does it mean to have it as an official standard?
Clear Implementation of Robots.txt
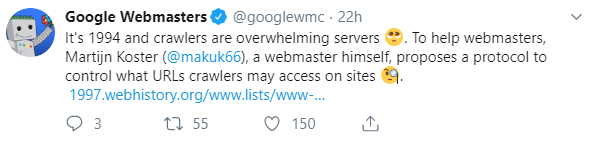
Through the Twitter account of Google Webmasters (@googlewmc), Google provided a series of tweets starting with reminiscing about the situation of web crawlers about overwhelming servers back in 1994, invoking the mention of Martijn Koster’s proposal of the protocol to control URL crawlers.
Aside from the original 1994 Standard for Robot Exclusion document, Koster’s 1996 historical description about the method for web robots control is the resource acknowledging the submission of the Robots Exclusion Protocol as an Internet Draft specification. The internet isn’t as developed in the 90s as it is now, so having the opportunity for webmasters to control the way their content is accessed is a pretty big deal back then.
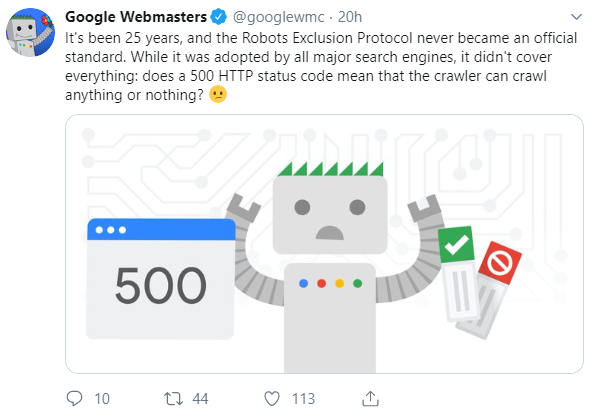
Back in 1996, it was regarded as a “work in progress” and I think it still is, given that there are webmasters who are puzzled by how the process truly works. Transitioning from the ambiguous de facto standard means that open-ended interpretations will come to an end. Even though the new proposal would not change any rules created since 1994, it would bring clarity to the “undefined scenarios for robots.txt parsing and matching,” according to Google.
“The proposed REP draft reflects over 20 years of real-world experience of relying on robots.txt rules, used both by Googlebot and other major crawlers, as well as about half a billion websites that rely on REP. These fine-grained controls give the publisher the power to decide what they’d like to be crawled on their site and potentially shown to interested users.”
Search engines have fully utilized the use of the REP but there are still some areas that haven’t been covered, which is why the proposed draft of the standardization will hopefully bring about a clearer explanation on the way Robots.txt works. Google, together with webmasters, other search engines and the proponent of the REP Specification, submitting a proposal to the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) means that this is a significant effort to extend robots exclusion mechanism as it can now be governed by a technical standard body.
Further Innovations from Webmasters
Together with the announcement to make the REP an internet standard, Google also considered the work of developers in parsing robots.txt files. Google’s robots.txt Parser is now an open source through their C++ library. You can find the robots.txt parser in Github, and they have also included a testing tool as part of the open source package.
With over 20 years of overseeing how webmasters create robots.txt files, this supplemented the internet draft passed to the IETF. This means that search engines are readily available to help web creators to experiment and innovate on the net; all for the purpose of creating unique and engaging content for better user experience.
The active development of the protocol just means that there will be further updates for the modern web. Again, they would not be making changes to the established rules for the robots.txt. The updated rules can be seen below:
- Any URI based transfer protocol can use robots.txt. It would not be limited to HTTP anymore. Additionally, it can be used for FTP or CoAP as well.
- Developers must parse at least the first 500 kibibytes of a robots.txt. The act of defining a maximum file size highlights that the connections are not open for too long, alleviating unnecessary strain on servers.
- A new maximum caching time of 24 hours or cache directive value if available, this will give website owners the flexibility to update their robots.txt whenever they want, as crawlers aren’t overloading websites with robots.txt requests at the same time.
- Disallowed pages are not crawled for a reasonable long period of time when the robots.txt file becomes inaccessible due to server failure.
In addition to that, they have also updated the augmented Backus-Naur form which is also included in the internet draft which will better define the syntax of the .txt file, this is a move that can help developers parse the lines accordingly.
A Challenge to Robots.txt Creation
Google partners are ecstatic over this development because the research and implementation of the protocol is no joke.
This initiative has been well-researched with over 20 years of data to back it up so it only makes sense that webmasters follow the lead and make the Internet a better place through the protocol. One thing that is notable to mention is that the draft of the proposal states that the crawlers should allow special characters.
With this, it should be a call to action to webmasters to be careful about the values they encode in the .txt file. There are instances when typos prevent the crawlers from understanding the command from the webmaster.
Hopefully, having standard rules for creating robots.txt will embolden site masters to be vigilant in creating the protocol for their site. Robots.txt has been used in over 500 million websites which is why it is important that you give optimal attention to it.
Key Takeaway
Robots.txt specifications have also been updated to match the REP draft submitted to the IETF. I suggest that you should read up and focus on making a clean Robots.txt file for your site. Controlling search engine crawlers to achieve better indexing and rankings can only go so far if you do not do it right.
As you innovate and make your site the most optimal it is, learn about the mechanisms and how to make it work in your favor. What are your thoughts on this recent draft to make the Robots Exclusion Protocol an official standard?