Learn SEO: The Complete Guide for Beginners
What should I learn first in SEO?
Quick Answers: If you’re just starting out, you don’t need to do a deep dive into all the factors and algorithms that Google uses to rank a website. However, I recommend starting with the key components of SEO, which are technical, on-page, and off-page SEO factors. I also recommend studying up on how to do keyword research, your niche, and what content is valuable and interesting for the people in your industry and your customers.
Overview
SEO is an essential skill for marketers and an essential practice for anyone trying to break into the online landscape. With SEO, you can increase the targeted traffic to your website from search engines.
Here in the first part of our learn SEO series, Learn SEO: The Complete Guide for Beginners, you will be introduced to the different kinds of SEO, the most important ranking factors, notable algorithm updates, and so on. You will also learn about the different SEO tools that you can use for research and monitoring.
What is SEO?
SEO is an acronym for Search Engine Optimization. It is part of digital marketing, and it is the process of making your website a better-ranking site in the search engines than other websites with the same niche or market as yours.
Why is SEO important?
There are two main reasons why SEO is important.
Search engines matter
Search engines are a big way to get traffic to your site—that is if you have the right content. People who surf the internet almost always look for information they need. If your site provides that information but it doesn’t show up on the search engine results page, then your site is next to useless.
Visibility is key
SEO makes your site more visible to internet users. Marketing is all about getting more people to see what you’re selling or promoting. SEO is like marketing in the search engine. It is a great way to tell people who use search engines: “Hey, look, I’ve got what you need.” And mind you, Google receives about 8.5 billion queries per day.
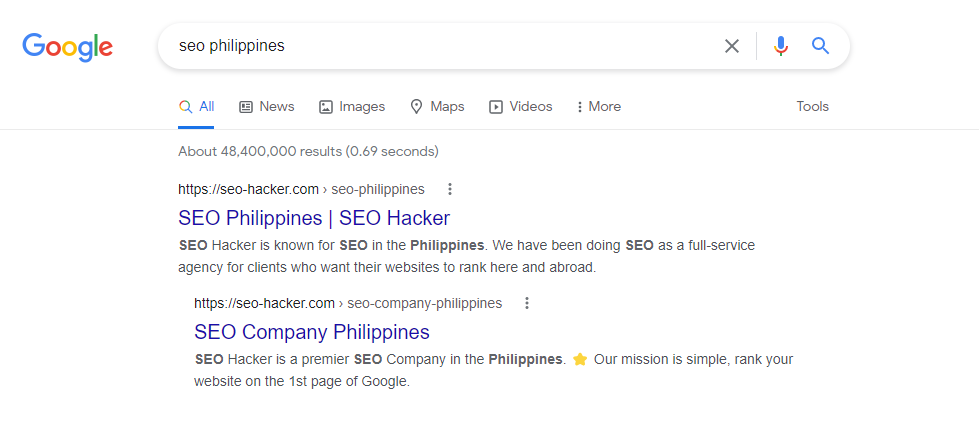
For example, when you Google “SEO Philippines,” you will see that we are the #1 search result. This tells you that we are the most relevant result for your query.
And Google is far from being the only search engine out there.
So, what now?
Basically, that’s what SEO is. SEO is making it easier for your target audience to find you. It’s marketing by keyword competition in the search engines.
How does SEO work?
Let us say that you needed some information on retargeting marketing, so you type in the query “What is retargeting marketing?” on Google. There are a couple of websites that show up to answer your query, and you notice that Website A gives you the answers you need and a pleasant user experience. Website B however, even if your user experience there is also pretty smooth, it also doesn’t really answer the question you posed (in fact, it’s just trying to sell you something).
For Google, it would make more sense to rank Website A as it is the one that gives the user most what they need. This is the simplest way to explain it of course, as there are over 200 ranking factors that Google uses in their algorithm.
How long does it take for SEO to work?
Truthfully, SEO can take a while to work. It all depends on a lot of factors including how much content and optimization you work into your website right out of the gate. Ranking at the top of Google is no easy feat under any circumstances, but with SEO it can take around 4-6 months to feel the effects.
We at SEO Hacker stand by the idea that SEO is a long-term investment, especially because SEO isn’t just about reaching the top spot at the SERPs, it’s also about staying there.
Going back to our “SEO Philippines” keyword, we can proudly say that we have been ranking #1 for more than a decade. That is what you want to achieve when you do your own SEO.
Understanding search engines
A search engine is a web service that searches for information online and pulls up the relevant web pages into a collection of Search Engine Results Pages or SERPs. They help to minimize efforts to find information and help to find the best ones more easily.
For example, imagine if you have to learn about email marketing for your work. Without a search engine, you would have so much difficulty finding information on the internet as there is no one service that would bring the necessary information to you immediately. Most likely there won’t even be any information online about email marketing because people won’t give the time and effort to create web pages that would remain stagnant due to the lack of visitors.
A search engine has three main functions: index, retrieve, and rank.
Index
When you own a website, you know it’s all code. The web browser’s function is to display those codes in a format that is friendly to human eyes. For example, here’s the code version of my last blog post:
Read: 10 Types of Digital Marketing Channels to Try [In 2022]
That’s why meta tags are actually read by search engines even if they don’t appear on an HTML browser. Because it’s part of the code. And the search spiders crawl the code, not the browser display.
As I mentioned earlier, one of the search engine’s main functions is to index a website. Search engine spiders do most of this work.
All the code in your website has to be read in order for it to be indexed successfully. If it’s not read well, it will show up distorted in Google’s database which we can see through its cache on the search results.
Retrieve
Retrieval is basically when the search engine gets a query, looks over its index database and regurgitates whatever is relevant to the search terms (or keywords). It is a critical function of the search engine for us end-users because this is what we use search engines for.
When you make a search query, the search engine goes through all its data in its index database and looks for the keywords matching your search query. When it has found all the relevant ones, it will retrieve it out of its database and proceed to rank it before releasing it to you.
Retrieval is critical because some search engines still read meta tags such as your meta description during its retrieval process—though it is not used for ranking nor does it affect ranking in any way. Still, it has some bearing on the SERPs when it gives you the result.
All search engines retrieve data the same way. It’s the ranking where they differ.
Rank
Why Google is the foremost search engine in our generation today is because of their superb ability to remove spam and unrelated results in their SERPs. They filter it out in their index and make sure that spam and other least-related websites and information are filtered out to rank last—or worse, sandboxed.
Note: Google never confirmed the existence of the Sandbox, but experience says otherwise.
Google’s ranking system is composed of algorithms that look at 200+ factors that we can put in three major categories (that we will break down later):
- On-page factors
- Off-page factors
- Technical factors
These three categories are then computed by Google to gauge how high a webpage’s page rank or authority score is. Page ranking is how Google gauges your website’s authority and reputation. A webpage with a high page rank value is deemed more important and therefore it is more likely to rank higher than those with lower page rank.
Google had a patented version of PageRank that was treated by SEO practitioners before as the single most important factor in ranking. Now, it’s different. Although PageRank still exists and it definitely still matters, we can think of it now more as an authority metric that can let us know how important a link would be if it came from a domain with a high authority score. Semrush has a really good article on this topic.
Sometimes when a lower page rank has more relevance to a query than that of a higher one, the lower one will take priority. Rankings now depend on Google’s data in relevance to the user’s query. In the end, the searcher still has control on the search results depending on how good and specific he/she is in defining his/her query.
This is why we believe in optimizing for users, not just search engines.
Google algorithm updates
According to Google:
“With the amount of information available on the web, finding what you need would be nearly impossible without some help sorting through it. Google ranking systems are designed to do just that: sort through hundreds of billions of webpages in our Search index to find the most relevant, useful results in a fraction of a second, and present them in a way that helps you find what you’re looking for.”
As mentioned earlier, algorithms are what comprises the ranking systems, and they look at hundreds of different factors. Algorithm updates ensure that Google will deliver only the highest quality results to its users, and so we prioritize optimizing the factors that these algorithm updates tell us are the most relevant.
Caffeine
There were algorithm updates before Caffeine, but I want to start with this. The Caffeine update finished rolling out in 2010 and was created to speed up the indexing process and provide 50% fresher results for searches.
Since the web was growing at an enormous rate, Google decided to switch up their indexing process from checking the entire web at one go to checking portions of it and updating their search index continuously. This is one of the main reasons why we focus on content freshness—to stay relevant to the users and the search engines.
Panda
Google wants their search engine to give only relevant web pages to their users, and avoid content that is irrelevant or spammy. Unfortunately, there were sites that functioned as content farms—meaning they employed plenty of freelance writers that would churn out content to satisfy Google’s freshness requirements brought about by the previous update.
So, Google released their Panda update to combat websites that had bad backlink profiles and spammy content, effectively ensuring that the surviving websites would be ones that actually created quality content.
Penguin
Google Penguin is an algorithm update that was released in 2012. The update helped lessen the search presence of websites that use unethical link building techniques and keyword stuffing, while rewarding websites with high quality content.
Hummingbird
The Hummingbird update is a search algorithm that was released in 2013. This update improved how Google reads search inquiries by using the algorithm to understand each word of the search term. This helped Google understand user intent better as well, making long-form searches much more effective, and ensuring that the whole search term is taken into account.
RankBrain
RankBrain is a machine learning algorithm rolled out in 2015 that made ranking a lot more competitive than before. See, RankBrain is AI—and it was built off Hummingbird’s ability to recognize “things” instead of “strings” (which is also why pages can rank for multiple keywords instead of just one). Context now plays a role in Search as well, which means that SEO practitioners need to optimize as close to user intent as they can.
All in all, RankBrain ensured that only the most meaningful and relevant results would be served to the users, so the goal now is to become an industry leader and not just someone who writes blogs to bring in traffic.
Because of RankBrain, we’re more focused on comprehensive, relevant, evergreen content that will answer our target audience’s questions.
Medic
The Medic update penalized Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) websites, especially those with little to no Expertise, Authority, or Trust (E-A-T) signals. These sites were referred to as YMYL as they contained potentially life-altering content, such as health and medical websites.
The websites that were hit the worst were websites giving unsubstantiated medical claims or advice, and retail sites that had no medical studies to back their claims.
BERT
With the BERT model, Google became able to understand words in the search query in relation to each other, instead of interpreting them independently of one another like before.
The primary target of the BERT update were long-tail keywords, so that Google can assist its users in finding useful information.
This update stressed the importance of creating content and optimizing for users and not just search engines. If the search engine can understand complex words and sentences but the user cannot, then it would be useless for the search engine to present your content to its users.
Page experience update
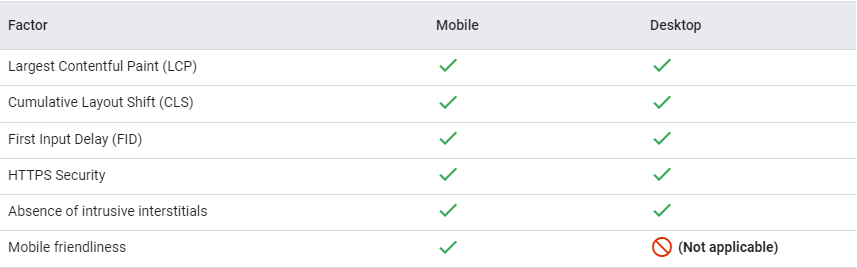
The page experience update started rolling out in June 2021 and was completed at the beginning of September. The update is pretty straightforward: user experience has become a ranking factor, which is why we don’t just optimize content—we also optimize for mobile-friendliness, core web vitals, security, and ad experience.
According to Google, the rollout of the desktop version of this update finished last March 4, and the factors will be the same except for mobile-friendliness.
MUM
With Google MUM, the SERPs are expected to be a lot more visual, and the SEO industry is expected to place more importance on semantic search in general. According to Google, “Across all these MUM experiences, we look forward to helping people discover more web pages, videos, images and ideas that they may not have come across or otherwise searched for.”
Google’s search results are about to get even more context-dependent with a fine-tuned understanding of the most relevant information pertaining to their users’ needs. Although MUM’s rollout is quite gradual, knowing what this model can do can help inform your SEO strategy.
This is far from being an exhaustive list, but these are the algorithm updates that we take into consideration the most. We’ve found that optimizing for these has been the most effective in terms of SEO strategy and has streamlined our optimization tasks greatly.
Kinds of SEO strategies
There are three kinds of SEO strategies that I will be discussing here: black hat, gray hat, and white hat SEO.
To properly learn SEO, it’s important that you know what kinds of techniques fall under each of these so that you can prevent yourself from accidentally engaging in shady SEO tactics and end up getting penalized by Google.
Black hat
SEO is a practice that has existed for more than a decade. This length of time has allowed webmasters and SEOs to create innovative, unique, and effective strategies to take their websites to the top of the search results. Even though it is a relatively straightforward practice, it allows limitless possibilities and immense flexibility in terms of creating and innovating new processes and strategies. This is one of the main reasons why SEO will always be one of the best digital marketing facets anywhere in the world.
However, with these possibilities and flexibility come people that aim to achieve results in a shorter time frame. This is all because SEO is a long-term game—monumental results will only be gained through multiple months or years of effort. This is why people aimed to take advantage of the system, doing unethical practices to gain results faster—in other words, a shortcut. These unethical practices in the industry came to be called black hat SEO, which led to the ethical and upright practices to be conversely called white hat SEO.
To make it simple, white hat method is the good, clean way which makes quality, competitive, informative content it’s main weapon and tool, while black hat method is the ‘how-to-go around the rules’ method which uses doorway pages, invisible texts, keyword stuffing and comment spamming. It abuses artificial and technical loopholes as it’s main route to attain higher page rank which search engines are not happy about.
Some examples of black hat SEO are:
Keyword stuffing
Keyword stuffing is the practice of packing keywords into your site even when it makes no sense. It greatly lowers user-friendliness, information relevance, and quality of your site in exchange for a temporary increase in rankings. While this is something that Google can sniff out much faster nowadays, it is still very likely that users can encounter this issue.
While it is important for keywords to get ranked, it is also equally important to ensure that the content you would be writing comes off as natural and informative instead of something that would only generate a temporary spike in traffic.
Invisible texts and links
Using invisible texts is simply putting some keywords with the same color as your background so that it would be invisible to site visitors. At a glance, these web pages may look similar to regular pages, but a simple hover of your mouse (or by pressing CTRL+A) would reveal the hidden text. This is an attempt to add more characters and keywords to a web page to increase rankings, and it is also a tactic that tries to take advantage of Google’s algorithm.
Likewise, hidden links are another issue as well. There might be times when you will encounter a page that suddenly takes you to a different page despite not being able to see the link on which you clicked on. This negative link-building technique not only aims to mislead but also create low-quality web pages that would not get traffic.
These are practices that Google can instantly track down and penalize, but many web pages that apply this technique remain.
Doorway pages
Doorway pages are web pages that are merely put up as dummies. This is done for search engine spiders to crawl links and keywords for the main site (which the doorway page would most probably point to). Usually, the users would never see or find these pages.
Cloaking
One of the oldest black hat SEO techniques, cloaking is the act of misleading users into content they did not search for. Imagine searching for a keyword like “school” and clicking on a link to a related website, only to lead to an entirely different set of content. This is a practice commonly done to generate traffic to a website. However, this technique is misleading, which seriously dampens the user experience, and can lead to Google penalizing your website.
Website quality and authority are measured through trustworthiness and informative content, which means any form of deliberate misinformation will always be negative on a website. It is best to make sure that your links get to the right pages, as this would not only allow GoogleBot to crawl, but also bring in more traffic and much-needed link juice.
Link farms
Links are essential in generating traffic to any website and allow users to discover and connect new content. This makes a link building team a very crucial element to any SEO effort, as tactics like guest blogging and outbound linking are some of the best traffic-generating methods. However, some people have created methods to abuse this system, leading to web pages whose purpose was to only place an abundant amount of links, with barely any relevant and informative content.
These web pages are called link farms. While most of these websites have been made harder and harder to find thanks to Google’s strict standards, these remain a common issue. Other than having low-quality content, some of these links can lead to malware and other similar kinds of software that can harm your computer.
Sneaky and shady redirects
Along with hidden text and links, there are also instances where web pages would contain sneaky and shady links in places you might not be able to notice upon first glance. Some of these links are modified expired links aiming to capitalize on the link juice of the previous link to gain traffic. While 301 redirects are a standard SEO practice, abusing the system would lead to penalties you wouldn’t want to happen.
This type of practice is commonly found on websites that are ad-heavy, meaning users would most likely inadvertently click on them. A notable example are websites that offer illegal downloads, as almost all kinds of shady and malicious links would be present whether you clicked them or not. There’s a good reason that these websites do not show up in SERPs that often, and Google would make sure that these would be penalized accordingly.
Comment spamming
Comments are some of the best ways to create meaningful discussions that encourage interaction and expand your connections. It is also a sign that your content has constant readers and viewers. This makes comment moderation an important task to ensure that harmful comments will be screened and removed, and only productive and informative ones remain.
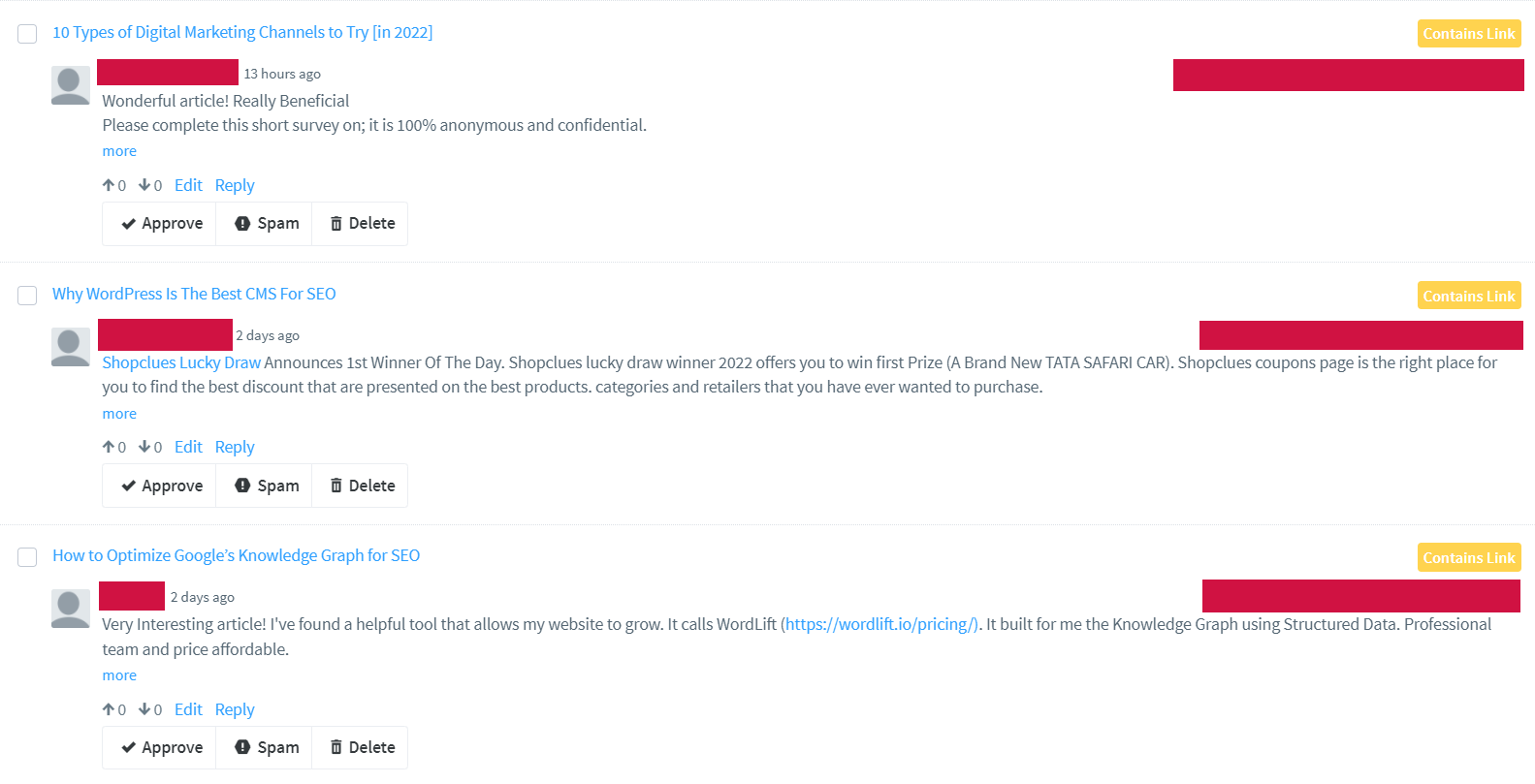
Unfortunately, the comments section can also be used to post spammy content that only aims to try and get links to their websites. While adding links in comments isn’t exactly a negative practice, creating comments with the intention of solely trying to get traffic is something that should be avoided. There are times when these comments can come en masse, crowding the comments section with nonsense that people would only avoid. This negatively affects traffic, causing it to get penalties, which means that you would not be appearing on search that often anymore.
The best solution to overcoming this issue is to use comment moderation tools, as they would help you filter out comments more efficiently, making sure that spam would not be present. This also means avoiding having a dozen or so comments that would instantly get posted on your content.
Automatically generated content
Auto-generated content is a type of content that has been generated through the use of programming. Its main goal is to automatically generate content to manipulate a website’s search rankings while putting in less effort, as these aren’t made to provide helpful and relevant information to users. Google does not condone these types of strategies and will immediately penalize a site that has been found to use auto-generated content. Some examples are:
- Content that are nonsensical but still contains keywords that the website ranks for
- Published auto-translated content (using tools) that was not curated by humans
- Content that has been created through the use of synonymous words
- The use of obfuscation techniques to publish content that has no value but are still full of keywords
Participating in link schemes
The very first algorithm that Google used to rank websites in the search results pages is PageRank and link schemes are strategies that specifically try to manipulate PageRank. Some examples of link schemes are:
- The buying and selling of links. From the exchange of money to the offering of goods and services for links, these are all violations of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines
- Excessive link exchange from the same website
- Excessive guest posting using anchor texts that are filled with keywords used by your website
- Automated link creation
There are other examples of link schemes but these are the most common ones that are done by most black hat practitioners.
Participating in affiliate programs without adding sufficient value
Google has always strongly recommended that webmasters should publish fresh, original, and informative content. They give extra importance regarding this recommendation for websites actively participating in affiliate programs. This is because most websites participating in affiliate programs use the product’s description used by other websites involved with the same affiliate program. This piece of content that is visible in different websites across the internet makes Google deem them as using copied content.
Creating pages with malicious behavior
In relation to shady and sneaky links, the pages in which they are present mostly contain malicious behavior. Other than illegal download sites, there’s a host of other harmful content (e.g., phishing, Trojan software, other damaging computer viruses) which attempts to get important and private information from you or damage your computer.
Some of these pages are disguised as blog posts that try to promote or sell something, but would only have links within it that would lead to low-quality websites. The only way to manage all of this is to observe proper content management and create quality content that would not lead to any harmful software that might affect your users, or illegally distribute anything that can cause any legal implications.
Gray hat
Gray hat SEO is a set of techniques and strategies that generally don’t adhere to Google’s guidelines but can still be considered acceptable. It is the middle ground between white hat and black hat SEO. It is technically legal, but risky.
Does it work?
Yes, it could work for you if done the right way. It is generally not recommended to use some of these techniques because they have a manipulative nature like black hat SEO, but in essence does not violate Google’s guidelines. Because of that, there are still risks of getting penalized by Google. But when done the right way, you could reap benefits similar to white hat SEO strategies.
Gray hat SEO is more common than you think. For example, Google recommends getting links organically (i.e., publish great content and get people to link to your content). In a perfect world, that would work just fine. But in reality, you would still need to pull out some stuff from your bag of tricks to get some links to your new content.
Is gray hat SEO still worth doing?
My answer would be yes, but as mentioned—with moderation and proper execution. Here are some gray hat SEO techniques that people are still doing:
Domain grabbing
Domain grabbing is the process of buying expired domains and linking it to your website. This practice is popular for those who want to improve their backlink profiles fast and easy and accelerate the process of ranking.
Usually, domain grabbing involves buying old domains that already have good backlink profiles and established authority. This strategy works best if the old content of the old domains is relevant to your website’s niche. But if you plan on buying random domains without checking if their link profiles are good, it could do more harm to your website.
The process is pretty simple; check if the expired domain has good backlinks using Ahrefs, buy the domain, then do a 301 redirect of the whole domain to your website.
Link building in Web 2.0 sites
Today, most of the websites on the internet are what we call Web 2.0 sites. These are websites where users have the ability to collaborate with the webmasters. These are websites that are driven by its community.
Why is this considered a gray hat tactic? For Google, links where users have the control of its approval, anchor text, placement, etc. is unethical. However, the purpose of Web 2.0 sites is collaboration and reward people who contribute by allowing them to link out to their own websites or resources.
Examples of Web 2.0 are Wikipedia, Quora, Medium, WikiHow, and Reddit. When done right, it could help establish expertise in your niche and could contribute to your website’s overall E-A-T.
The best way to go about these types of websites is to genuinely contribute. Take answering questions seriously, contribute valuable and factual content, and never ever spam and leave keyword-rich anchor texts around.
Social bookmarking
Social bookmarking websites are places that allow users to submit and share their content for promotion and bookmark other content that fits their interest for later reading. Websites like Folkd and Mix (formerly StumbleUpon) are popular because not only can you dump your links around but could also get some referral traffic.
Social bookmarking sites won’t hurt your website generally since they typically give out nofollow links. Social bookmarking is actually a good way of promoting new content. A good measure would be to sign up for 2 or 3 sites. The thing that makes this practice acceptable is that you still need content for it to work.
But just like any SEO strategy, there are some who abuse it. There are social bookmarking websites that are built solely for dumping links and these are the ones you should watch out for.
Link exchange
Link exchanges have been around ever since Google announced PageRank in 1998. Webmasters started to realize that they could easily grow their link profiles faster if they exchanged links with each other.
Generally, link exchanges are fine. If both webmasters have content related to each other, why not link to each other as resources right? It is when people abuse this strategy that it goes bad. To Google, the most ideal way of getting a link is organic: people read your content, people like your content, people link to your content.
Having friends or partner webmasters is good and sharing some link juice is nice. But if you and your friends are linking to each other with each and every post you publish, then you have a problem.
Guest blogging
Guest blogging or guest posting has been around for a long time and it is probably one of the most common SEO techniques that are still being used. The main purpose of guest blogging is actually great. Create partnerships with other webmasters and contribute content to their audience. It is a great way of building good links and to promote yourself.
However, there are some instances where guest blogging can be a gray hat SEO technique rather than a white hat SEO technique.
There are tons of websites that were only made to be guest blogging websites and are just used to pass on domain authority. Guest posts with excessive linking and spammy anchor texts are discouraged too.
When doing guest blogging, focus on contributing to a website that has value. Don’t do guest blogging for the sole purpose of getting a backlink. Do your best to provide valuable information to the website’s audience.
White hat
White hat SEO is the use of tactics and strategies that follows all search engine guidelines and policies. A defining trait of white hat SEO is making the users priority and not the search engines. Your main goal should be to learn SEO that is white hat in nature.
White hat SEO is the complete opposite of black hat SEO. Any practice that aims to improve a website’s search rankings while still keeping its integrity and is in line with search engine guidelines is considered to be an example of white hat SEO. Some specific white hat strategies are:
- Content written for the users
- Fast site speed
- Mobile-friendliness
- Easy site navigation
- Proper and natural use of keywords inside the content and meta tags
Importance of white hat SEO
It is important for webmasters and SEO professionals to only do white hat SEO since practicing any other methods can get their websites penalized or banned. This will result in a massive traffic drop for your website and that means losing valuable audience and customers.
White hat SEO is also a webmaster’s primary means to consistently stay in the search rankings since a website’s authority and rank can only go up once you practice white hat SEO. Being visible for the right keywords for a long time can only give you benefits—increased lead generation and conversions. That’s why white hat SEO is the way to go.
Why content isn’t enough for white hat SEO
A phrase that’s heard in the SEO industry quite often is “Content is king.” To an extent it’s true, but that doesn’t mean it’s the only factor that we should take into account. Content may be king, but what’s a king without its queen and their subjects? All the other factors that a Google spider verifies such as meta tags, image alt text, keyword density, backlinks, etc. are just as important.
White hat SEO focuses mainly on content—basically on how user-friendly, informative, and useful your content is. When your content is good, people will talk about it in different social media channels and that will lead to a massive increase in traffic. It will also help your rankings since content that satisfies those three factors is ranked higher in the search engines.
White hat SEO is the way to play it safe.
- It obliges in all of the terms of agreement of social media; and
- It implements good, clean, Google-approved strategies in order to gain higher page rank and get better search engine visibility
Compared to black hat SEO, the white hat method will ensure your brand’s good reputation on the web and will enable you to be visible for a long time.
If you treat your online reputation with importance, then it’s important for you to choose the white hat method. The only drawback of white hat SEO is that it takes longer for clients to see your results. Businesses pay for fast, easy-come results. They don’t pay for slow, time-consuming processes which will have them wait for the results. It is important for you to communicate to your clients that white hat SEO takes up time but the results will pay dividends.
Here’s a table taken from marketing agency SilverDisc that explains the difference between a white hat and black hat approach to SEO:
| Black Hat | White Hat | |
| Content and Links | Search Engines | Humans |
| Visibility to Humans | Hidden | Visible |
| Quality of Work | Hidden | Visible |
| Search Engines | Enemies | Nothing / Friends |
| Domains/Brands | Disposable | Cherished, Primary Domain |
| Site & Relevance | Apparently Improved | Actually Improved |
| Results | Yes, “Short” Term | Yes, “Long” Term |
| Ethical Techniques | No | Yes |
| Legal | No? | Yes? |
If you are trying to build your brand or company online, then white hat SEO is what you need.
SEO ranking factors
In this section I will be discussing the various SEO ranking factors that you should learn about.
On-page SEO
On-page SEO is the practice of optimizing a webpage for search engines and users. An on-page SEO audit is when you crawl your webpages to check for areas of optimization. For example, you can check your title tags, headers, keywords, and other things that could help the search engines and users understand your webpage better.
SEO auditing is an important foundational tactic that all who want to learn SEO should know about. Search success can’t be achieved if you don’t know what to look for and what to apply in a website. Instead of enumerating the key on-page SEO factors, I’ll teach you here how to look for them.
Since this is a beginner’s guide, I’m using the homepage of the Leadership Stack website as an example. If you didn’t know, Leadership Stack is a digital marketing podcast I created as a space for discussion with other entrepreneurs to help Filipino entrepreneurs improve their leadership, teamwork, and profits.
Since I did not build the website for it—my team did—I thought it would be great to share with you my process as I perform my own site audit.
Note: You can keep this part open and follow the instructions as you conduct your own on-page SEO audit.
You can use tools for this job, but I advise doing it manually so you can really get to know the website you’re auditing. Tools can help, but they can only get you so far.
An on-page SEO audit does not need to be done every day. However, it is advisable to perform this task regularly to ensure that the websites you’re handling are at their most optimized. It is also highly recommended to perform this task whenever a new client comes in so you know exactly what you’re working with.
Before you begin
You will need two things: a findings document and a checklist. It’s good practice to prepare your materials before starting an audit so that you can proceed in a systematic manner, which makes the audit quicker.
Create your findings document first
You can pick whichever format is easiest for you, but here is a template:
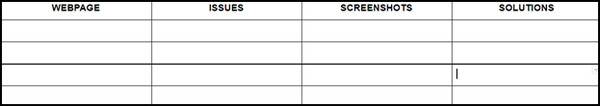
Download: On-page SEO Audit Template
I like preparing my document first so my output is clean and easy to understand instead of having to rearrange my findings after auditing a website. It also helps me be more methodical in my work.
Your audit checklist
Before we get into it, you need to know what to watch out for first.
- Check the keywords
- Check if the title tags are appropriate for the page
- Check if the headers are correct
- Check for keyword placement
- Check the pictures for alt text
- Check if the links are updated and visible
- Check for meta descriptions
You don’t need to follow these in order, just make sure to refer to them so you don’t accidentally neglect any of these points.
Onto the site audit
Now that you have your table and checklist ready, it’s time to get down to business and learn SEO.
Keywords
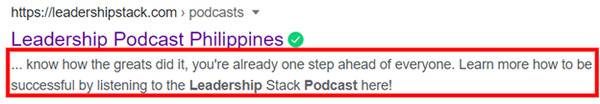
If you’re checking a website that is up and running, this might be a little difficult to do. However, search intent plays such a huge role in SEO that it’s integral to check these things. If you search for specific keywords, would you expect to find the website you’re auditing? For example, if I Google “leadership podcast Philippines,” should I expect to find the Leadership Stack website in the SERPs? If the answer is yes, then that’s good and you can check the rest. If the answer is no, then it’s time to do a little keyword research.
Title tags are one of the most important ranking factors, so it’s integral that you include your keyword in the title tag. If your keyword shows up in a user’s search query, then the search engine will show your page because it sees your page as relevant to the user. Plus, Google says that “It’s often the primary piece of information used [by the end user] to decide which result to click on,” so it’s crucial that you have a well-written title tag.
Another reason why it is crucial to have an optimized title tag is due to the Google update that caused the “titlepocalypse.” Although the title tags have been reverted to their original state for now, it is still highly advisable that they accurately describe your page and answer the users’ queries so that if Google again decides to generate titles, they would be based on what you have already written.

The title tag is the title of your webpage. It lets the users and the search engines know what the webpage is about. Before you even write the contents you think about the topic first. In the same way that it guides the rest of your article, the title tag also guides the content of your webpage.
Headers
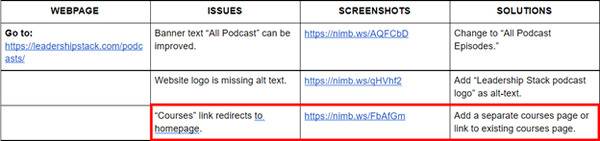
Next, check your headers. In this example, it’s the homepage banner. It is the first thing that the people who land on your homepage sees, so it’s important that you make a good impression.

It’s also a good idea to check headers (among other things) to ensure that they are spelled correctly and don’t have any grammar mistakes.
Fixing the grammar won’t directly affect rankings, but it will improve user experience and give you some credibility in the user’s eyes. No one likes going to websites that look like they haven’t been proofread.
Next, check if the main header of your page is in H1. The headers of your page help organize the content both for the search engine and the users. Think of your academic papers back in school. Instead of having blocks of text, you use headers to help your reader identify the sections of your paper. That is what your headers do.
If your page does not have a banner (like a blog post, for example), then the main text in your page should be in H1.
So, the main header should be in H1, then the sub-headers will be in H2, H3, and so on and so forth. You can check the headers of this article to see what I’m talking about.
Lastly, check your headers for keywords. Your main goal is to still make the page as understandable and contextual as possible for the search engine and the user, so it’s good to incorporate your relevant keywords to the headers.
Keyword placement and LSI
Since I’m checking the homepage of a podcast website, I don’t have huge bodies of text to sift through. But if we think of a homepage as your introduction to your users, then you need to make sure it ranks in search engines.
In this case, I check for keyword placement as I check the other elements of the webpage, such as the H1, title tag, meta description, image alt text, and body text. Keyword placement pertains to important areas where keywords should be found.
As important as placement is, you also have to check for the coherence of the content of your page. This is where Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) comes in. Think of it this way—when writing about a certain topic, you ensure that the words and phrases you use are connected to the topic you chose, right? In my case, I don’t have to keep repeating “Leadership Stack” all over my homepage, because there are other words such as “podcast episodes” as well that will signal to the search engine (and the user) that this page is about podcast episodes on leadership.
Image alt text
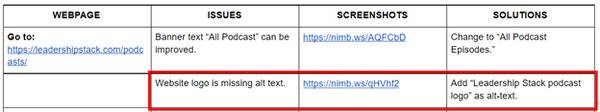
Having your company or brand logo on the webpage is highly recommended as your website is usually the lead’s first engagement with your brand. It’s important to check it for alt text.
![]()
To check, simply right-click the image, click “Inspect,” and search for the alt text in the code. It will look like: img alt= “ “
The alt text is what shows up when your website doesn’t load an image properly. It’s also what informs the search engine of what the picture is about so that it shows up during an image search, so it’s important that you give it the relevant keyword to help it rank in image search.
Don’t just check the logo, but the other relevant pictures in your webpage as well.
As I inspected the Leadership Stack logo, I saw that it doesn’t have a proper alt text, so that goes into the table.
Buttons and links
It is important to check your buttons and links to make sure they are redirecting to the right webpage. Broken links cut off the link juice that could have been flowing to the different pages in your website. It can also give users a bad experience and negatively impact your website’s authority.
There are tools available that can help you find broken links faster, but if you’re manually doing the on-page SEO audit, you can simply click on each button and link to check.
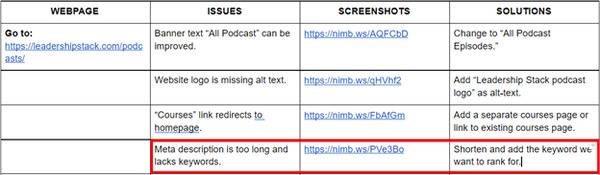
When I made this audit, I found that the “Courses” link at the page footer simply redirects back to the homepage. So, I noted down in my table that there is currently no existing “Courses” page to be used as a destination for this link.
![]()
I added it to the list with my proposed solution.
Now, the “Courses” link heads to masterclasses you can take.
Meta description
The webpage’s meta description is the short snippet that explains the content of the webpage on the result’s page. It is not a ranking factor but it is important in attracting users to click on your website. It’s your first chance to give users a good impression aside from your title tag.
A good meta description must be less than 155 characters. It should include your webpage’s main keyword and give the user a window as to what your webpage contains.
As you can see above, the meta description is too long and lacks the keyword we are trying to rank for. And because it’s too long, a user will most likely not click on our link when they see the meta description because they didn’t have that window to our webpage. So, that goes into the table.
Done! Now that you know how to perform an on-page SEO audit, you can go ahead and check the other pages of your website.
Off-page SEO
According to Moz, “Optimizing for off-site ranking factors involves improving search engine and user perception of a site’s popularity, relevance, trustworthiness, and authority.” There is one major way to accomplish this: link building.
What are links?
According to Computer Hope, a link or a hyperlink is a “is an icon, graphic, or text that links to another file or object.” Links connect web pages to one another, making navigation easier.
There are three types of links that you need to know:
- Inbound links
- Internal links
- Outbound links
Inbound links
Inbound links are links from other websites that link back to your website.
Here’s a simplified version to help you visualize it easier:
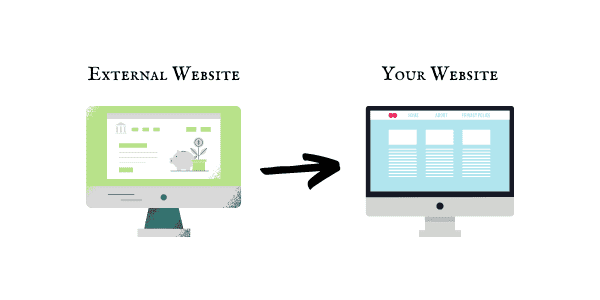
You can have multiple inbound links from one external website or referring domain, or one inbound link per external website or referring domain.
That’s why when you do a backlink analysis of your website, you will see that your website has so much more backlinks than it does referring domains.
For example, here’s the Semrush backlink analysis for SEO Hacker:
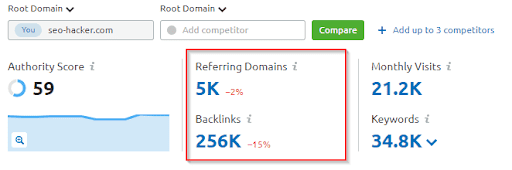
As you can see, in the past couple of months we’ve had around 5,000 referring domains, and we got around 256,000 backlinks from those domains.
There are two types of inbound links: dofollow and nofollow links. Dofollow links pass on link juice to your website, while nofollow links just point other users to your website but don’t pass on link juice.
Internal links
Next, we have internal links. Internal links are links you create between the pages of your own website. The link I placed in the anchor text “internal links” is an example of an internal link.
To visualize:
Internal links have a couple of uses:
- They make navigation between pages easier.
- They help search engine crawlers identify the most important pages of your website.
- They help establish your site structure.
So even if internal links aren’t as important for ranking as inbound links are, they are definitely important as they have their own functions that the other types of links can’t fulfill. By linking between your pages, you get to show your users and the search engine that your content in each webpage is relevant to one another.
Outbound links
Lastly, we have outbound links. These are links you place in your web pages that point to external websites.

Basically, you would want other websites to have outbound links that are directed to your website, making them inbound links.
Webmasters can also reach out to you and request for you to link to their website. Depending on the agreement, you can opt to give them dofollow or nofollow outbound links. When you have a nofollow link, make sure you add the code rel=”nofollow” to avoid passing on your website’s link juice.
Going back to our backlink profile:

You can see that we’ve referred to 868 external domains in the past couple of months.
What is link building?
Link building is the process of getting links back to your website from either the same website (internal backlinks) or other websites.
First off, you have to realize link building is one of the slowest processes that you have to go through to grow your site’s visibility as an SEO practitioner. Links don’t just pop out of nowhere. You have to earn them.
In link building, the most difficult yet most rewarding link to get would be inbound links.
Why do you need to learn how to build backlinks to your website?
Links are one of the fundamental ranking factors that we have. Think of it as word-of-mouth referrals. When you have many people referring your company to their friends and family, that means you’re building your credibility as a trustworthy company with good products and services.
But it’s not everything too. Links give your site more authority and reputation—giving it the power to strengthen the weight of its keywords.
Your keywords are your foundation, but your links make up the building. And what search engines usually look for is the building—then it makes its way down to the foundation. If your building looks good and is tall enough for it to be easily found, then your foundation is given deeper consideration and trust because it can hold up a tall and well-made structure.
The idea behind this is easy: the more links to your site only means your site is referred to by that many other websites. It means that your site must contain something interesting to all those site owners/webmasters, thus people would most probably also find your content useful—therefore, search engines like Google refer you in their search engine results page (SERPs).
Factors to consider in building backlinks
Not all links are good for your site’s ranking. Some links can bring your site down. It’s not altogether devastating—but that only means you have to choose your links carefully. Picking links isn’t an easy SEO task. It’s like one whole module altogether.
In choosing where to get links, there are five major factors to consider:
First, you have to look at the domain authority of the website. Why? Because the higher it is, the more Google juice you can get from it.
Imagine getting a link from Ahrefs vs getting a link from an unknown website. The search engines will determine that your Ahrefs link is of higher quality than if you got some random link. That’s plus points for your website.
Niche
Second, look at the website’s niche. Is your site related to this website? If you’re not related, the links you’re gonna get from that site are next to useless.
How come? Because relevance matters.
This doesn’t mean you can’t get links from forums or directories, but make sure these aren’t low-quality, spammy websites.
Outbound links
Thirdly, look at all the outbound links the site is giving away. Too many outbound links can mean that you’ll be sharing with all the other websites that this site is linking out to—giving you less Google juice compared to sites with low outbound links.
Link sources
Fourth, look at all the sites it gets its links from. Are they reputable sites? Are they related to your niche? Maybe you can get links from those sites too!
Types of links
Fifth, look at the site’s links if they are nofollow links. If you’re trying to rank (especially in Google), nofollow links will not help. So you better look for sites that don’t put nofollow in their links.
Of course, nofollow links can still be useful in directing users to your page (meaning, helping you generate traffic), but dofollow links are still ideal because they pass on link juice to your page.
How to build backlinks to your website
There are many ways to get links. Some are effective in boosting your rank, some are effective in giving you traffic, and some are effective in wasting your time. Here are some of the ways you can build your backlinks:
Directory listing
One way of getting backlinks is to add your website to a reputable online directory. Matthew Woodward has a fantastic tutorial on how to do this one.
Basically, you choose a directory that has high authority and you submit your website to it. The trick here is to look for high-quality directories that are moderated, so you can be sure that the site is trustworthy and isn’t spammy.
Forum posting
Another way to build backlinks to your website is through forum posting. Again, make sure you look for high-quality, moderated forums.
For example, Reddit has a community called Big SEO:
Posting links here is surprisingly difficult, so you have to have built a relationship with this community before you can even link back to your website. That practice helps avoid spammy links.
If you don’t have a Reddit account, you can choose to use Quora. Same practice applies—make sure you don’t spam links. Answer questions and give suggestions honestly, and don’t link back to yourself unless necessary.
Guest blogging
This is probably one of my favorite ways to get backlinks, but it is arguably one of the most laborious. Guest blogging (or guest posting) entails researching reputable sites that allow guest posting, coming up with a topic, writing an article, and undergoing an editing process.
You also have to make sure that you follow the instructions of the website you’re trying to publish your article in. For example, if a website allows only two dofollow links to your website, you wouldn’t want to be dishonest and put three.
Link bait
Link baiting is the practice of creating content that is so relevant, informative, and awesome that other websites will just have to link to it. The goal of course is to have all your content be linkable to, but the reality is not all our content is this way.
To create link bait content, you can consider the following formats according to Semrush:
- Interactive assets
- Data-driven studies and other assets
- Long-form guides
- Visuals
- Controversial or talking-point content
For example, we created a report on the State of SEO in the Philippines for 2022 where we discussed the search landscape in the country, our improvements and predictions for the coming year, how we fared against our top competitors, and so on and so forth.

Download: State of SEO in the Philippines 2022
Those who find this incredibly valuable can link to it. You can also create infographics, videos, and other content that other users will see as worth linking to.
Link exchange
This is another one of my favorite ways to get links. It’s straightforward—you negotiate with a reputable contact to exchange links. For example, you can email them and say that you have a website with a high domain authority and you’re willing to give a dofollow link this month in exchange for a dofollow link to an article you just wrote.
This is also incredibly effective if you guest post a lot. In that way, you won’t be giving dofollow links from your website only (or ever), because you can link to them through the blog you wrote on another website.
Paid links
Paid links are one way to earn backlinks to your website, but they can result in harsh penalties simply because paying for links is manipulation of Google’s algorithm. This is definitely the easiest way to get a backlink, but it’s also the riskiest.
Crowdsourcing
If you don’t have plenty of time to guest post, you can opt to be contacted when companies or writers crowdsource answers for a report or an article they’re writing.
For example, SEO Hacker was featured in a recent report by Databox titled, “Campaign Reporting: How to Gauge for Long Term Effectiveness?”

This was the result of Databox crowdsourcing answers—and seeing that ours was worth including in their report.
Contacting webmasters
One of the most important things you should learn on how to build backlinks to your website is by contacting webmasters. For example, if you have an article that recently linked to their work, or if you noticed that they have a broken link in one of their articles, you can reach out and pitch your article as a replacement.
This is one of the most difficult ways to get links, but like guest blogging, it is one of the most rewarding. See, this isn’t as simple as emailing webmasters and expecting links in return, it’s getting noticed and building a relationship with them first.
We already know how important dofollow links are. If you were in their position, would you answer every single person emailing you for a link? No, right? You would answer only those whom you’ve seen have been interacting with your work consistently.
Internal linking
Lastly, we have to go back to internal linking. This doesn’t help your website in the same way as inbound links do as we’ve mentioned earlier, but it does help your site be more coherent and it generates traffic to the other pages in your website.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is one of the most exciting parts of learning SEO in my opinion and certainly one of the most crucial ones. There is a unique satisfaction you could get when you see Google indexing more and more pages of your website. At the same time, it feels like you’re walking on a field of landmines and one mistake can make your website virtually gone on search engines.
Sounds scary right? But don’t worry, just because it has “technical” in its name doesn’t mean you need to have developer skills to do it (although you will need assistance from a web developer from time to time.)
What is technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the process of optimizing a website to make it easier for search engines to crawl and index. Generally, it also includes any technical aspects of SEO. Not only does technical SEO guarantee your website appears on search engine results but it also highly affects your rankings.
The noindex tag is used to tell search engines to not show a specific page on the search results. Meaning if you have a great piece of content that is ranking really well and you accidentally add a noindex tag on it, it might disappear from the search results in a few days. Make sure that all of your important pages are indexable and only use the noindex tag when necessary. To check if a page has a noindex tag on it, you could simply go to its source code and find a noindex tag or install browser tools/extensions to make things faster.
Check your robots.txt file
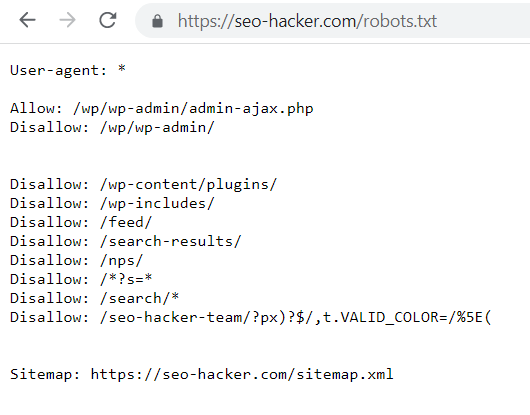
The robots.txt file is used to block search engine bots from crawling URLs that are specified in the file. You could use the robots.txt file to prevent search engine bots from entering certain parts of your website for security purposes or if you want a certain section of your site to not appear in the search results.
By default, your site’s robots.txt file can be seen by adding robots.txt on your domain: “https://yourwebsitehere.com/robots.txt”
Take note that once Google already indexes a page and you want to remove it from the search results, you should put a noindex tag on it first then block it through the robots.txt file to prevent it from being crawled again.
Secure your website
Installing an SSL (secure sockets layer) certificate on your website is one of the basic technical SEO optimizations that you can do. In fact, making your website on HTTPS is one of the most known minor ranking factors. Not only does this affect rankings but it may also affect user experience. Browsers may show a warning message to a user before entering a non-secured website. This can scare away users and it’s definitely a loss of traffic.
Submit your Website on Google Search Console
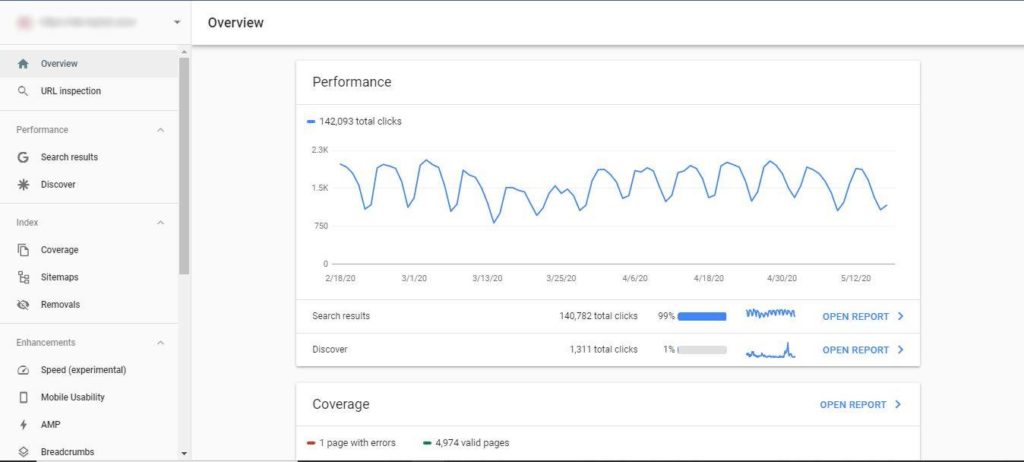
Submitting your website to Google Search Console (GSC) should be the first thing that you need to do once your website is up and running. Verifying your website on Google Search Consoles guarantees that your website appears on the search results. There are a lot of other benefits as well. Having your website on GSC allows you to monitor your organic clicks and impressions. Google will also notify you of errors when crawling and indexing your website through GSC.
Have a proper XML sitemap
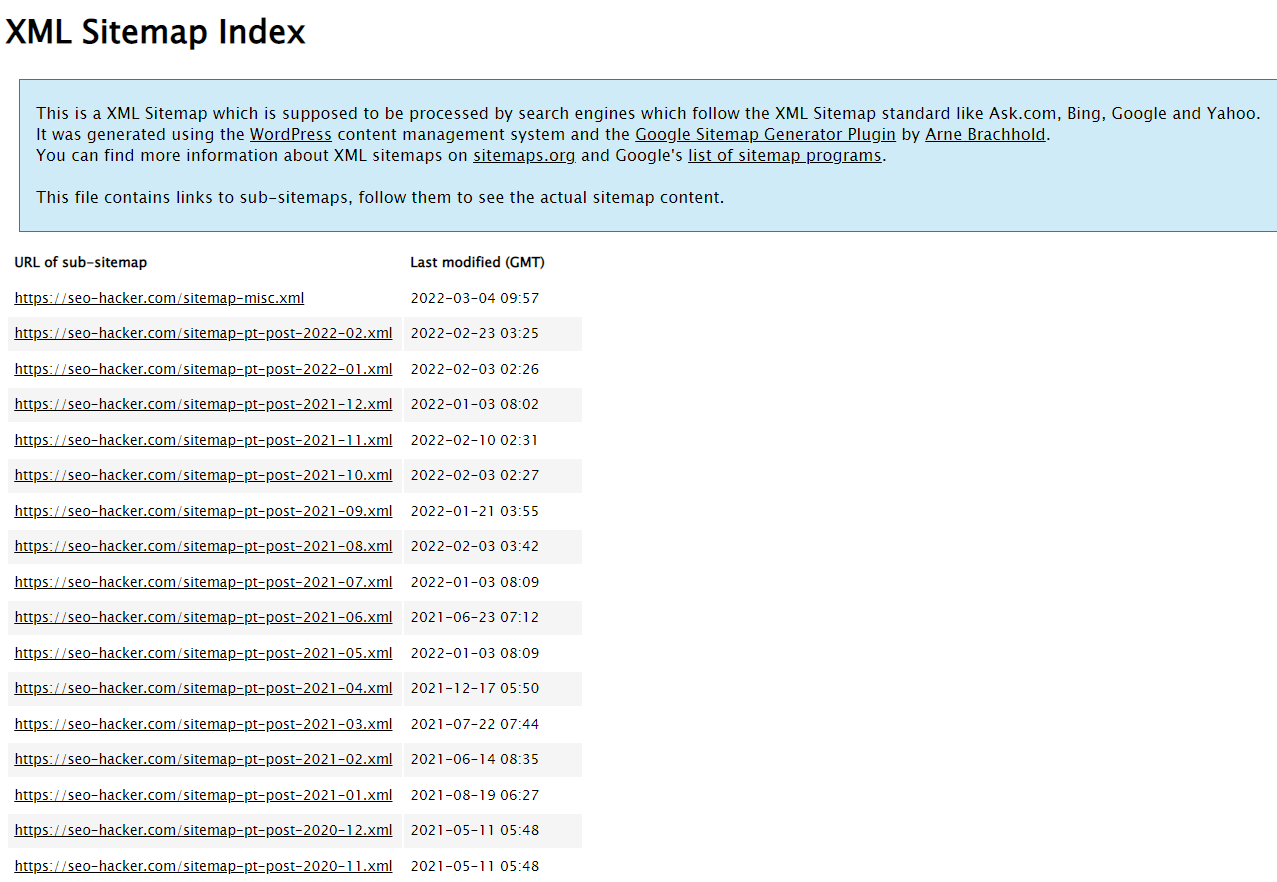
An XML sitemap file is the list of all URLs on your website. You then submit the sitemap to Google Search Console. Google treats all URLs in the sitemap as priorities for crawling. You could easily install an XML sitemap by downloading a plugin and from there, you can control what pages are excluded or included in the sitemap.
Optimize URL slugs
Optimizing the URL slugs of your pages is one of the easiest tasks to do for technical SEO and it is also an important one. It can affect your rankings since it is a place where you could add your target keyword and it makes your website look good for users. Optimize URL slugs by making it clean and easy to understand and refrain from using random letters and numbers.
Optimize site speed
Optimizing your website’s speed is always the way to go. Not only does it affect rankings, but also it affects user experience. You could use tools such as GTmetrix or Google’s PageSpeed Insights to check your website’s site speed and get recommendations on how you could further improve it.
For this one, you might need the assistance of a web developer on your team. But as an SEO, you could also do optimizations yourself such as compressing images, installing site speed optimization plugins, or moving to a faster hosting provider.
Make your website mobile-friendly
You might also need the assistance of a web developer on this one. Having a mobile-friendly website should be a top priority. Google gives high importance on mobile usability and it is known to be one of the top ranking factors. And since a large number of users come from mobile phones, it is best to make your website easier to use for them. Alternatively, you could use AMP or accelerated mobile pages to easily make mobile versions of your pages.
Remove links to dead pages
Linking to dead pages or 404 pages is a waste of link juice. Always be on the lookout for outbound links to 404 pages and make sure to update them and link them to live pages. If there is an internal link on your website to a page that you deleted or does not exist, search engines might be confused and you might see coverage errors on your GSC report. Use SEO crawlers to find links to dead pages and update them immediately.
Look for orphaned pages
Orphaned pages are pages that are not linked from other pages of your website or are not part of your website’s link ecosystem. This makes it hard for search engine bots to crawl and index these pages. You could use SEO crawl tools like Screaming Frog and Netpeak Spider to look for orphaned pages and check if these pages have any value.
Implement structured data markup
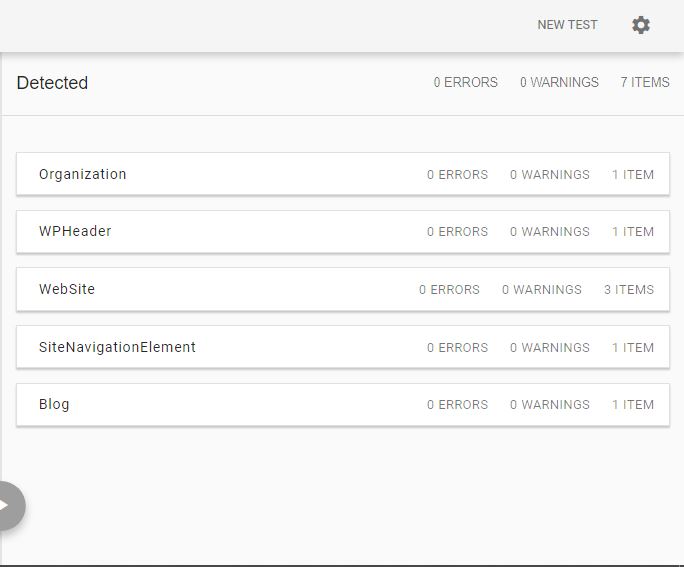
While structured data doesn’t affect rankings directly, it certainly helps search engines have a better understanding of your website and its contents. Having the right structured data markup enables your website to have rich snippets in search results and boost your click-through rate. You could use Google’s schema markup validator to make sure that the markup you implemented has no errors and is accepted by Google.
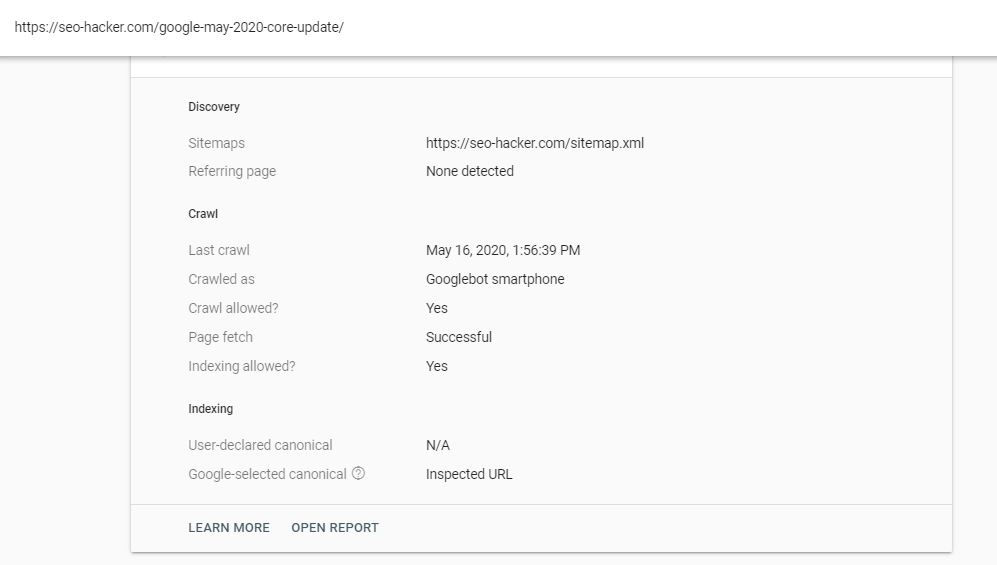
Canonical tags are known to be an advanced SEO strategy as it requires careful implementation. Like the noindex tag and robots.txt, improper canonicalization of pages in your website can massively affect how Google crawls and indexes your website.
A canonical tag is used to denote that a page has the same contents as the page it is canonical to. By default, all pages should be self-canonical. For example, this post: https://seo-hacker.com/google-may-2020-core-update/ should have the code <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://seo-hacker.com/google-may-2020-core-update/”> in it.
Should you want to set a different canonical to a page, you could use tools like YoastSEO or you could ask your developer to implement the code on different pages. In my experience, canonical tags are mostly used on e-commerce websites as they tend to have multiple product listings with minimal differences with each other.
Take note that if you want to check if Google is reading your canonical tags correctly, you can use the URL inspection tool on Google Search Console, click on Coverage and it will indicate the user-declared canonical and Google-selected canonical. Google always follows the user-declared canonical but in some cases, Google’s bot would select its own canonical because it may find similar pages on your website.
SEO tools you can use
Once you learn SEO, you will find that a lot of the work involves gut feeling and creativity. Those two things are irreplaceable by tools. However, there are some that are essential in helping you do SEO effectively. This section introduces you to a couple of those tools.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
Honestly, Screaming Frog is straight-up one of the most important tools you can use as you learn SEO (and even when you’re a professional) It displays data that will matter to you as an SEO professional.
It crawls and studies all your links: internal and external response codes, and URI. It also shows data about your on-site optimization such as title tags, meta description, meta keywords, H1 tags, H2 tags, images, meta & canonical. Not only that, you can filter the data display to see only the data that you’re concerned with.
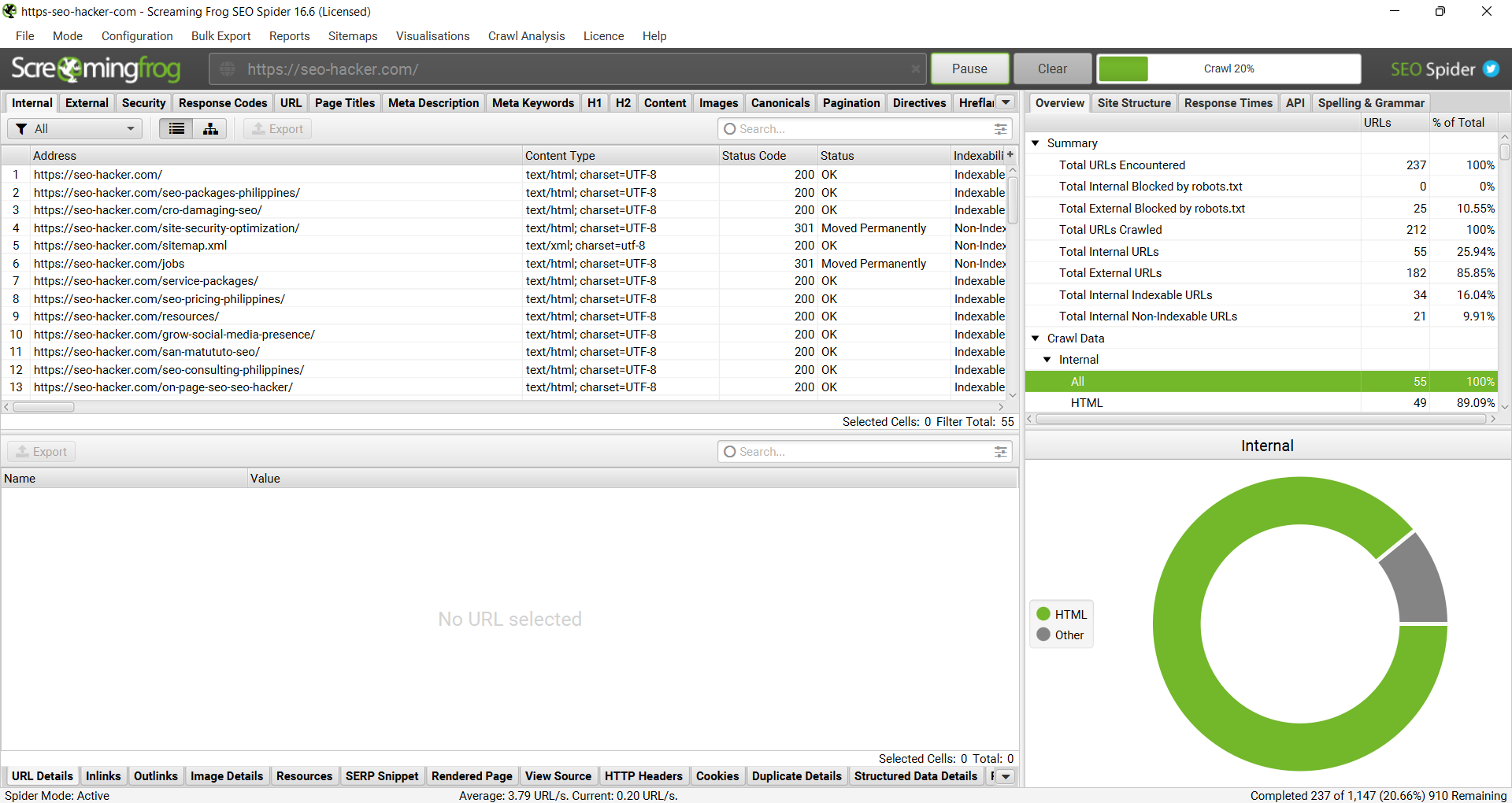
It’s very simple and easy to use. You don’t need to be a rocket scientist to navigate this tool and be familiar with its functionalities.
These are the different kinds of data that Screaming Frog can provide you with the links that it crawls in the URL that you enter.
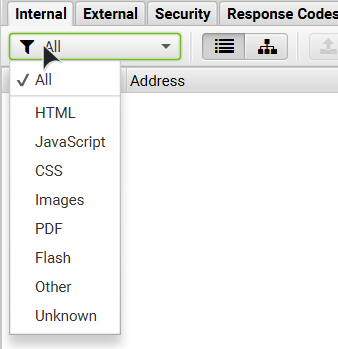
You can choose to filter the data that will be displayed to you in each and every category available.
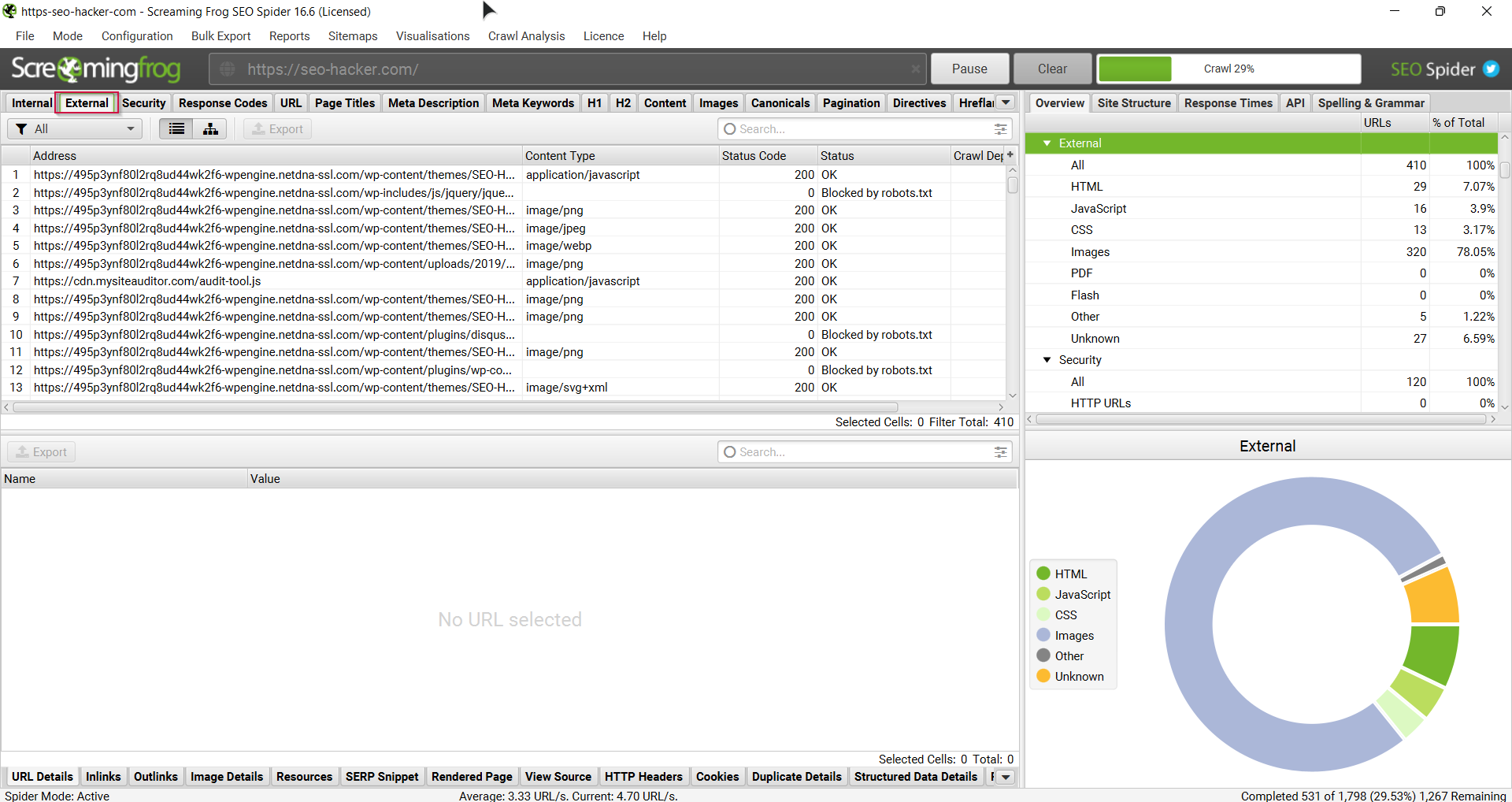
You can also do any of the following:
- View all the page titles inside your website. You can filter if you just want to see those that have missing title tags, long title tags (more than 70 characters), same as H1 tags, duplicate and/or multiple.
- View your images and the size of your image files. You can also see which ones are missing alt texts and which have over 100 characters in the alt text.
- Meta and canonical data are displayed. You can filter them as you like too.
- See all the inbound links inside a single link on your website.
- And a lot more!
Why do you need this tool?
There are lots of links inside a website and not all links are good. Sometimes there are broken links and you need to fix them or else it’s a turn-off to search engine spiders. This tool helps you look out for the obvious broken links that you have.
Sometimes you just need to check how a search engine spider crawls through your site. This tool helps you see which pages get indexed, which doesn’t.
You can also check out if your pages are missing canonicals or which of your images are missing alt texts. As you learn SEO, you get to see which areas in your website needs checking, and this tool can help make that job easier for you.
SE Ranking
One of the essential SEO tools that helps keep your performance in check is a keyword tracking tool that helps you monitor your rankings. These tools are SEO fundamentals that make sure that your strategies are working well and adjust accordingly to the latest trends and search engine updates.
Looking for a quality keyword rank tracking tool should be one of your top priorities as an SEO professional. With all the tools that we have in our SEO Hacker toolbox, we make sure that we only use the best tools available. One of these quality keyword rank tracking tools is SE Ranking, which is a tool that aims to provide updated and accurate rankings that you can regularly monitor. Before we begin this review, we would like to invite you and try the tool out for yourself by signing up for a free trial by going to this link.
Starting up
Upon signing in, you would immediately go to the Dashboard, where you would be able to access all of the features available. This is also the area where you would be able to view and monitor your rankings real-time. For those who want to begin tracking their website’s keywords immediately, the option to add your website is readily available.
Other key features that you can access are the Reports, where you can generate detailed reports for your team and clients. And Tools, where you can access even more features that help you perform various SEO tasks. You can also pause and continue keyword rank tracking to let you focus on specific keywords or click All Rankings and access all of it. You can also group these keywords together so that you would be able to track them much more efficiently, especially if you have a big number of clients.
Adding and tracking a website
Before you are able to track keywords for the websites you handle, you would need to add them to the database. The whole process has three steps and will only take you a few minutes to accomplish.
Step 1
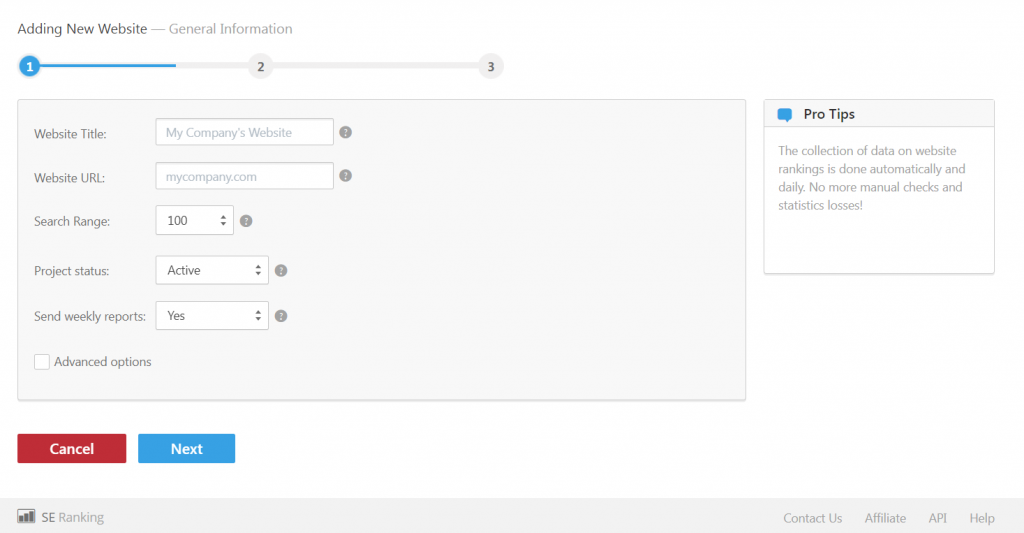
The first step is to enter the website title and URL, along with adjusting the search range. You can also change the project status by choosing between active and paused. Lastly, you have the option to send in weekly reports. Once you have all of the details sent in, you can proceed to the next step.
Step 2
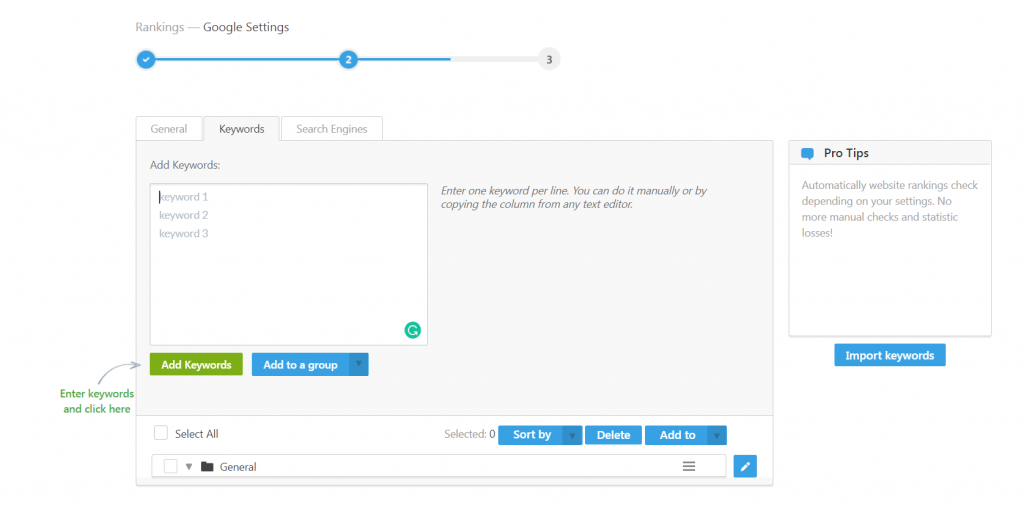
The next step is to add and group together keywords that you want to be tracked for your website. You also have the option to link your website to Google Analytics, which would provide you with even more search and website data.
Step 3
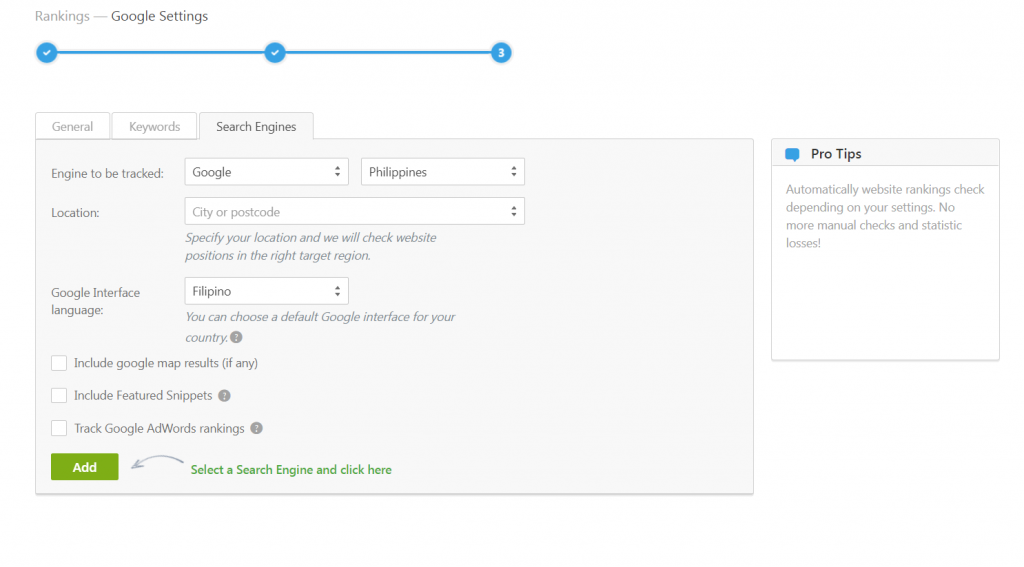
The third and final step is choosing which search engines would you want to track rankings on. You can also narrow down the location by picking a specific country and city in which to track your keyword performance. You can also change the interface language to conform with the local language, which comes in handy for both local and international SEO.
Website Tracking
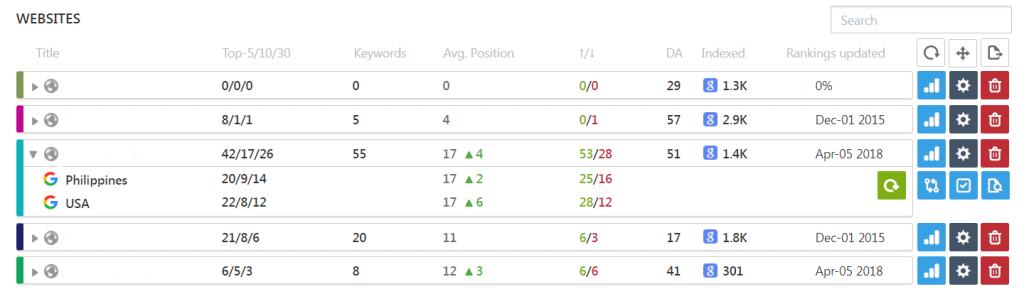
After registering your websites into the database, you can now track all of the keywords that you have entered. All you have to do is to view them into the Dashboard and click on the rankings button, which is the blue one on the right. You can also change your options by clicking on the gear icon or remove the website from the database altogether by clicking on the delete button.

Upon clicking on the website, you would go to the website overview, where you will be able to see all your keywords and their rankings. You can select different options to be able to see more detailed data, such as the rankings during a certain period in time, historical data, or which search engine would you like to monitor.
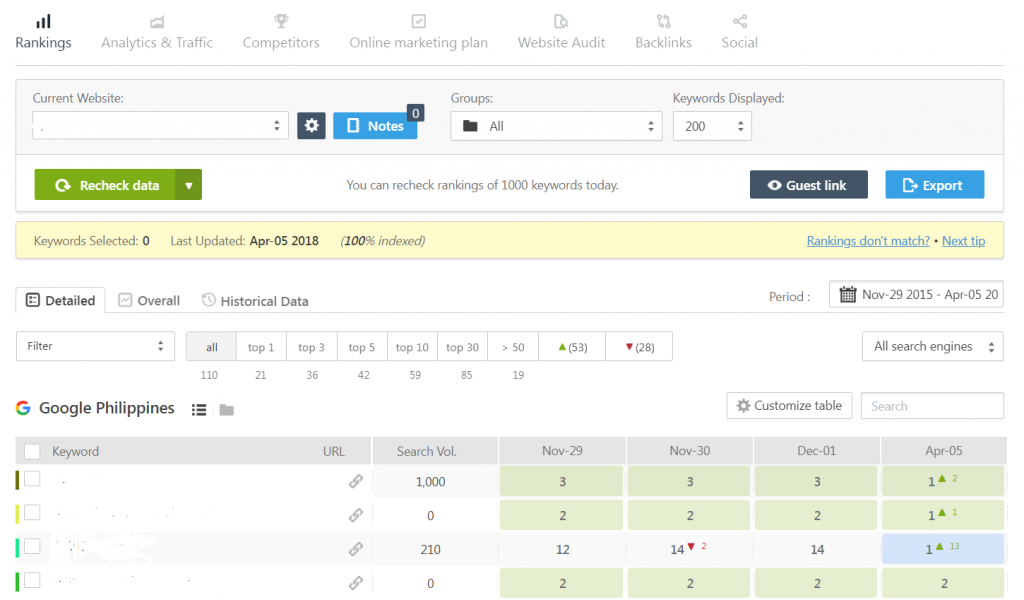
You can also take a deeper look into your analytics after linking your website to Google Analytics. This would allow you to see your traffic sources and average keyword position.
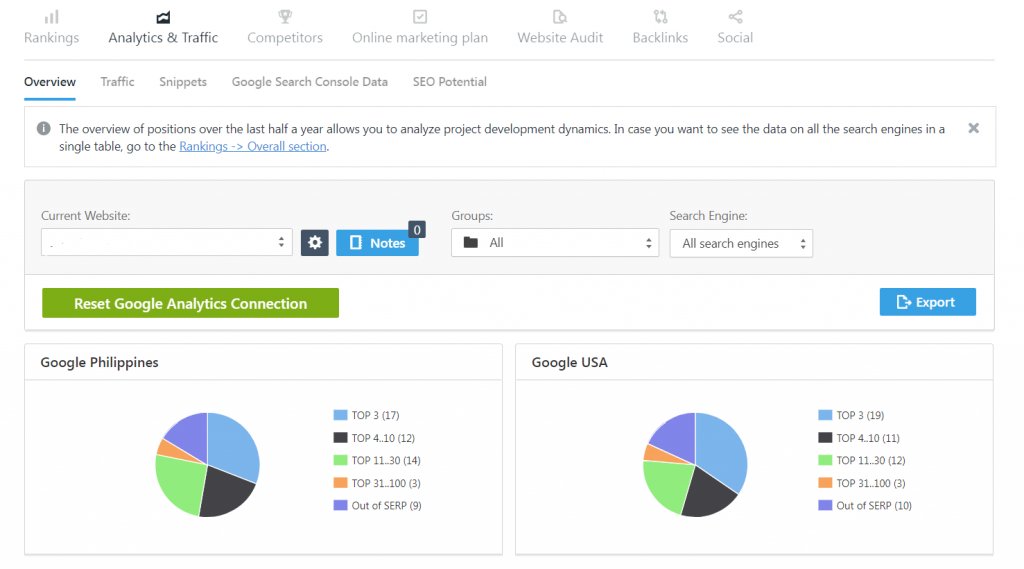
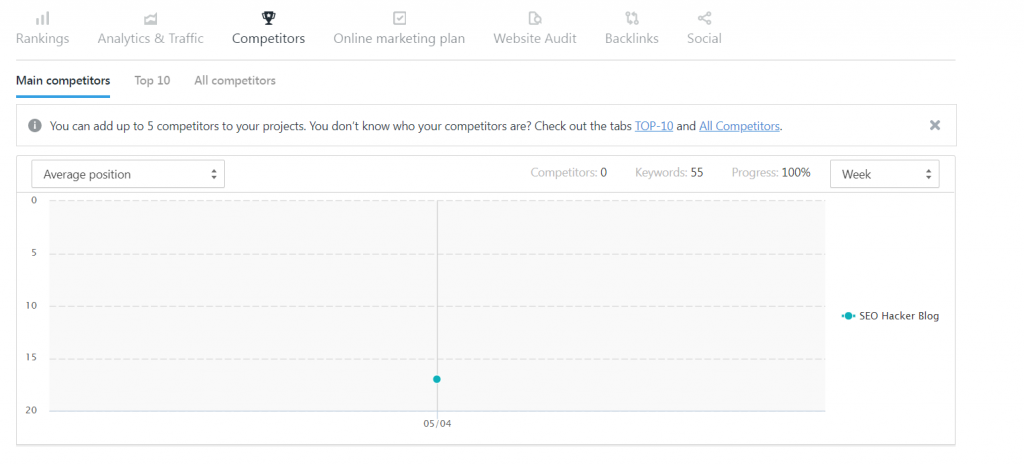
You can also perform competitor analysis and see how your competitor’s keywords rank compared to yours. This is an invaluable feature that keeps you in tabs with your competitors much more efficiently.
The last important feature of note is the Website Audit feature. This allows you to review and analyze your website, and evaluate its overall performance. This allows you to see what kinds of strategies and techniques are working, and the best steps you can take to improve your website.
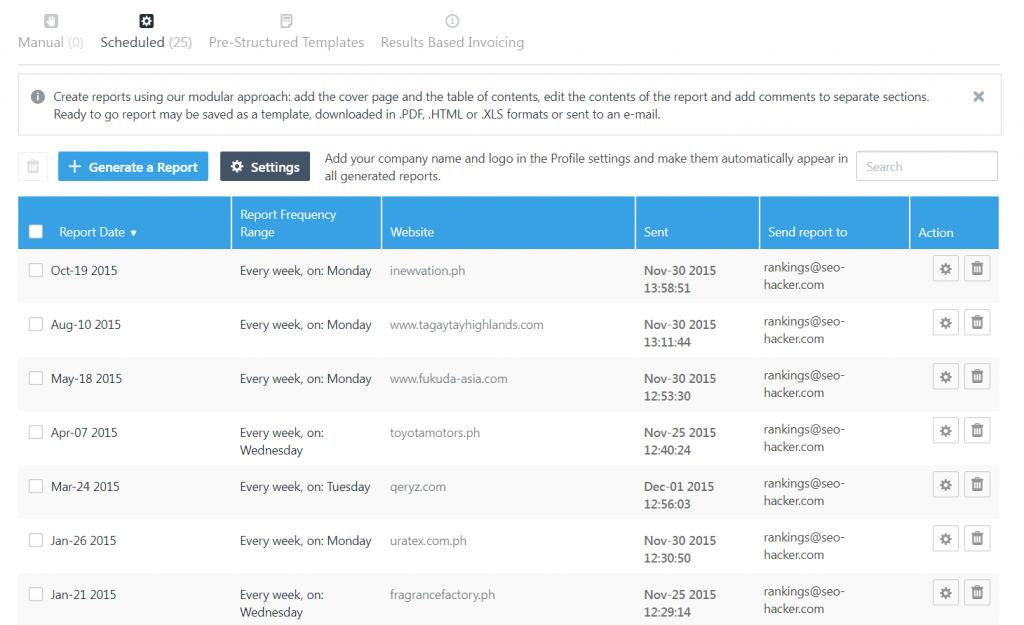
Reports
After looking into the data of your website, you have the option of sending a report to your clients for their reference. As previously mentioned, you can schedule these reports accordingly, ensuring that you would be able to deliver reports in .pdf, .html, or .xls format.
Tools
Along with the rank tracking features that the tool has, you also have a bevy of other tools to use as well. Here are some of the notable tools that stand out:
Backlinks Explorer
The Backlinks Explorer allows you to check the different backlinks on your website and list them down. This will allow you to check valid and invalid links.
Keyword Suggestion Tool
Keyword research is essential to finding the best keywords that would rank for your website. The Keyword Suggestion Tool allows you to find the best performing keyword for your website.
Competitor SEO/PPC Research
This handy tool allows you to monitor the amount of organic and paid traffic that your competitors receive. This tool is currently in beta, which means that we will be seeing a more refined tool in the near future.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is completely free and absolutely useful for you as you learn SEO. It helps you track user activity and informs the content portion of your SEO strategy. This includes how many users entered your website in a specific timespan, where those users came from, which pages they visited, what your top pages are, etc.
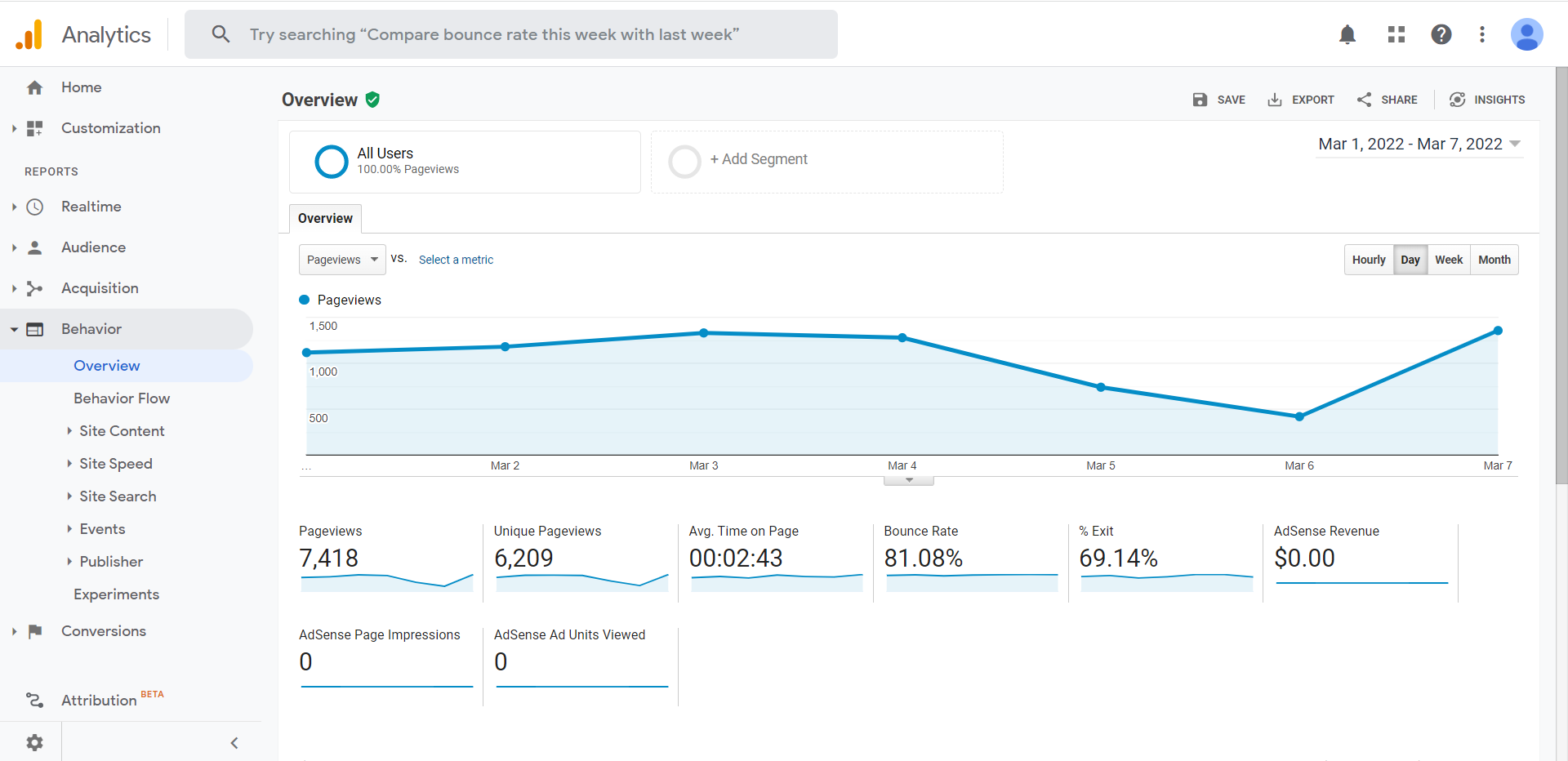
In short, Google Analytics is all about real data in your website. Data that you can translate into useful business intelligence and SEO strategy for your online campaigns.
Understanding the data
Google Analytics can get tricky, technical and confusing if you let it. Let’s keep things simple. Basically if you’re a person who just wants to know what your users are doing in your website, installing the tracking code is all you need. Only when you’ve installed the tracking code correctly will it be able to gather your user’s data. Once it has gathered data, it can show you the data when you visit your Google Analytics account again.
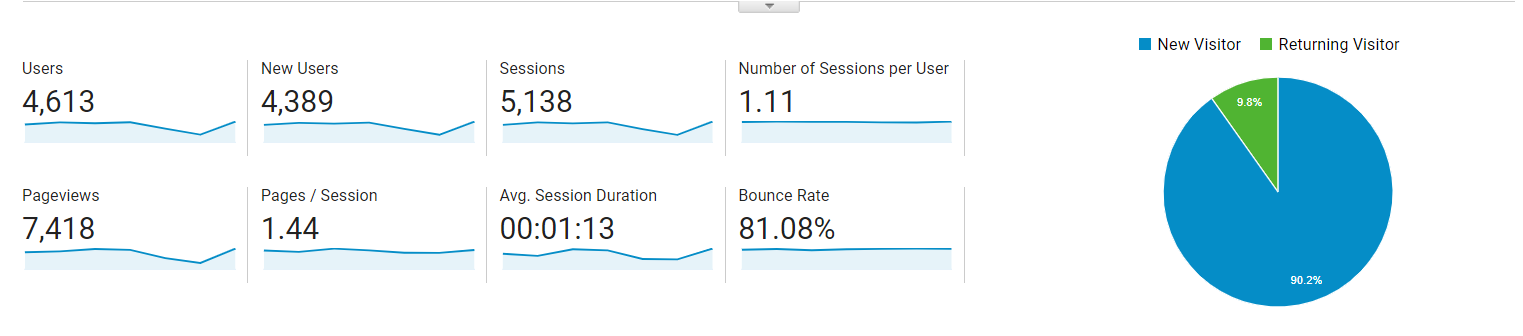
- Sessions are the number of times a user went in your website to look around
- Pageviews are the number of pages a visitor has looked at for the duration of his stay (for that day) in your website
- Pages / Session is simply Pageviews divided by Sessions
- Number of Sessions per User is the total number of Sessions divided by the Users
- Avg. Session Duration is the average time spent by your users in your website
- Bounce Rate is the percentage of your users going into your website and ‘bouncing out.’ Bouncing out can be defined as any action the user does that takes him out of your website in a specific time frame
These are just the basics. It gets deeper and deeper than this. There’s data manipulation, filtering, goal setting, and a lot more.
Key takeaway
There you have it: the basic things that you need to know to learn SEO as an absolute beginner. Learning SEO may not be a complete walk in the park, but once you get the basics down, the advanced portions will be easier to learn.
As I said earlier, the rule of thumb is to optimize for users and not just search engines. So long as you keep it in mind that you’re doing what you’re doing to make websites as awesome as they can be for people, then ranking in the SERPs should not be an issue.
Good luck!